Lamin T Cells
S3b this parameter correlates weakly with lamin a b or a b stoichiometry fig.
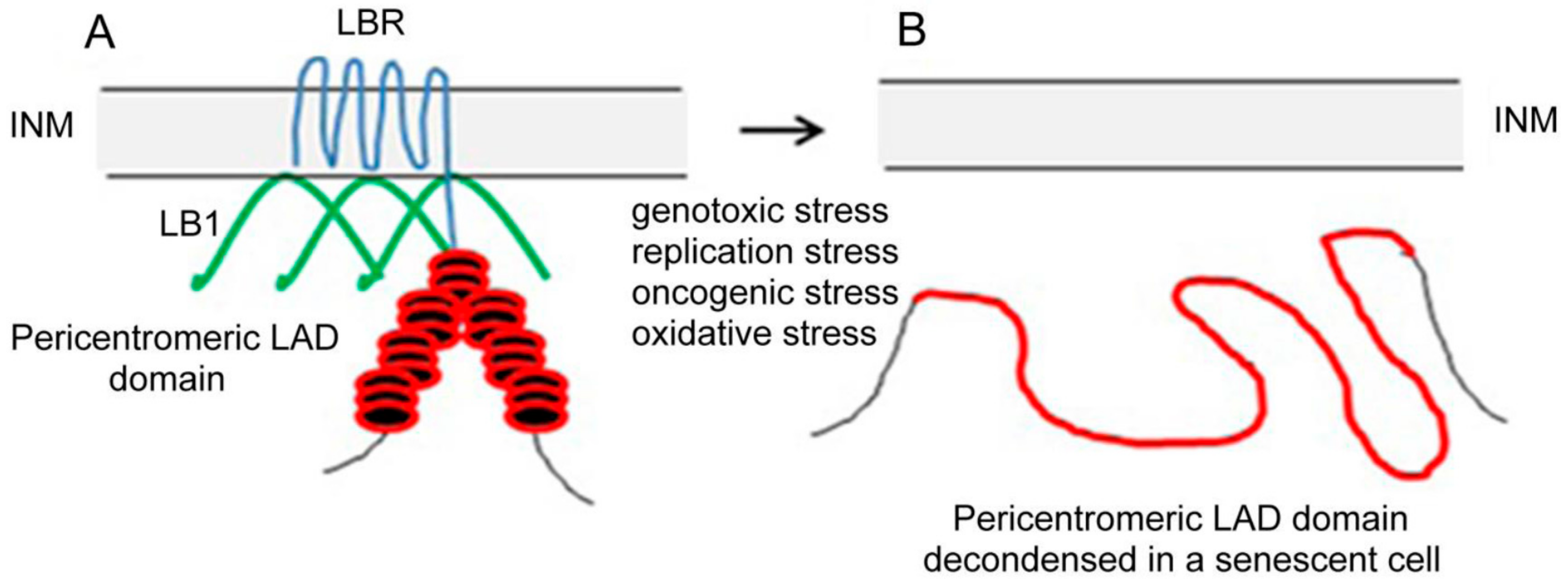
Lamin t cells. 27 the transient lamin a c expression observed upon t cell activation might be essential to regulate these cellular functions. Furukawa et al 1994. This new information regarding the range of lamins expressed in human fat cells provides an essential framework for attempts to understand the pathophysiology of. B type lamins are important for proper migration of epicardial cells and neurons and increased lamin b to lamin a ratio accelerates cancer cell migration through confined spaces.
A type lamins are encoded by a single gene lmna. Moreover a positive association between lamin b1 levels and. We propose that the increase in lamin a expression after t cell antigen recognition occurs in order to coordinate the process of t cell activation and that the. The role of lamins in t lymphocyte biology.
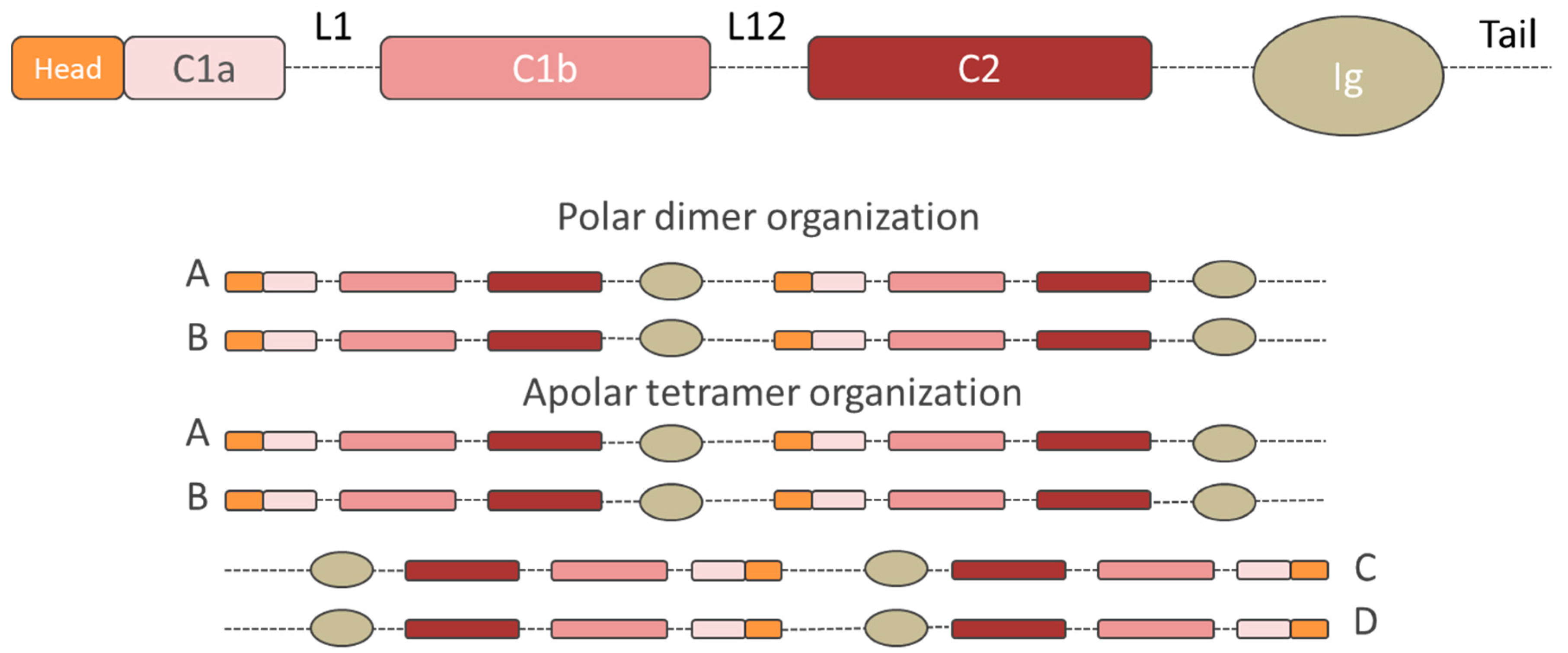
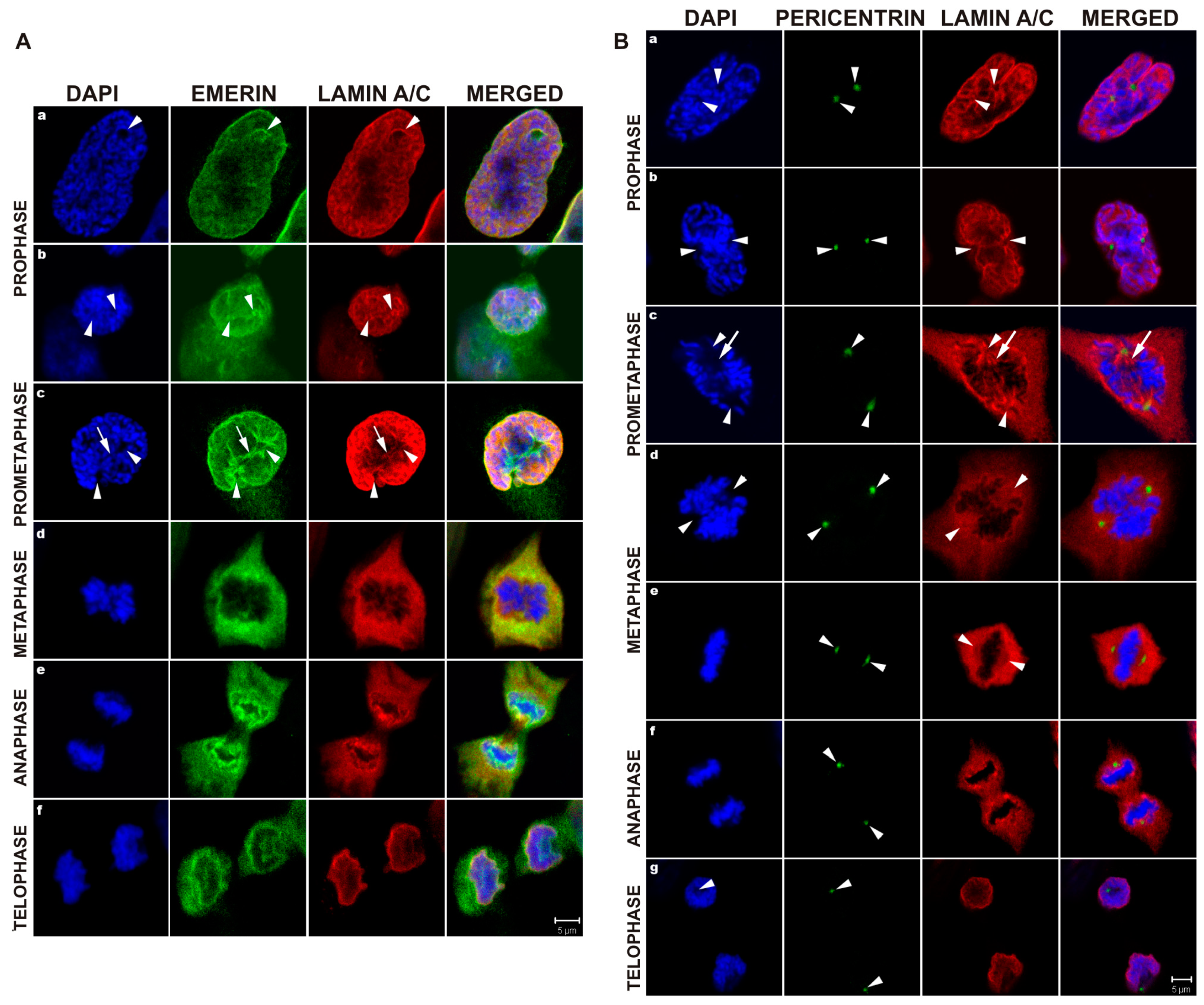
In mammals alternative splicing gives rise to lamin a and lamin c and the less abundant isoforms lamin aδ10 and lamin c2 fisher et al 1986. For example in mammalian cells the lamina is composed of up to five lamin isotypes three a types and two b types and there appears to be variability in the thickness of lamin b staining at the nuclear periphery within the same nucleus as seen by both light and electron microscopy belmont et al. Lamin proteins are involved in the disassembling and reforming of the nuclear envelope during mitosis the positioning of nuclear pores and programmed cell death. Lamin structure and assembly.
Although the general trend is that cd34 and t cells have a low a 1 2 and the extreme cell types in the lineage map such as high ploidy mks have a high a 1 2 fig. Cell migration requires reposition and reshaping of the cell nucleus. Mutations in lamin genes can result in several genetic laminopathies which may be life threatening. There are several different laminins.
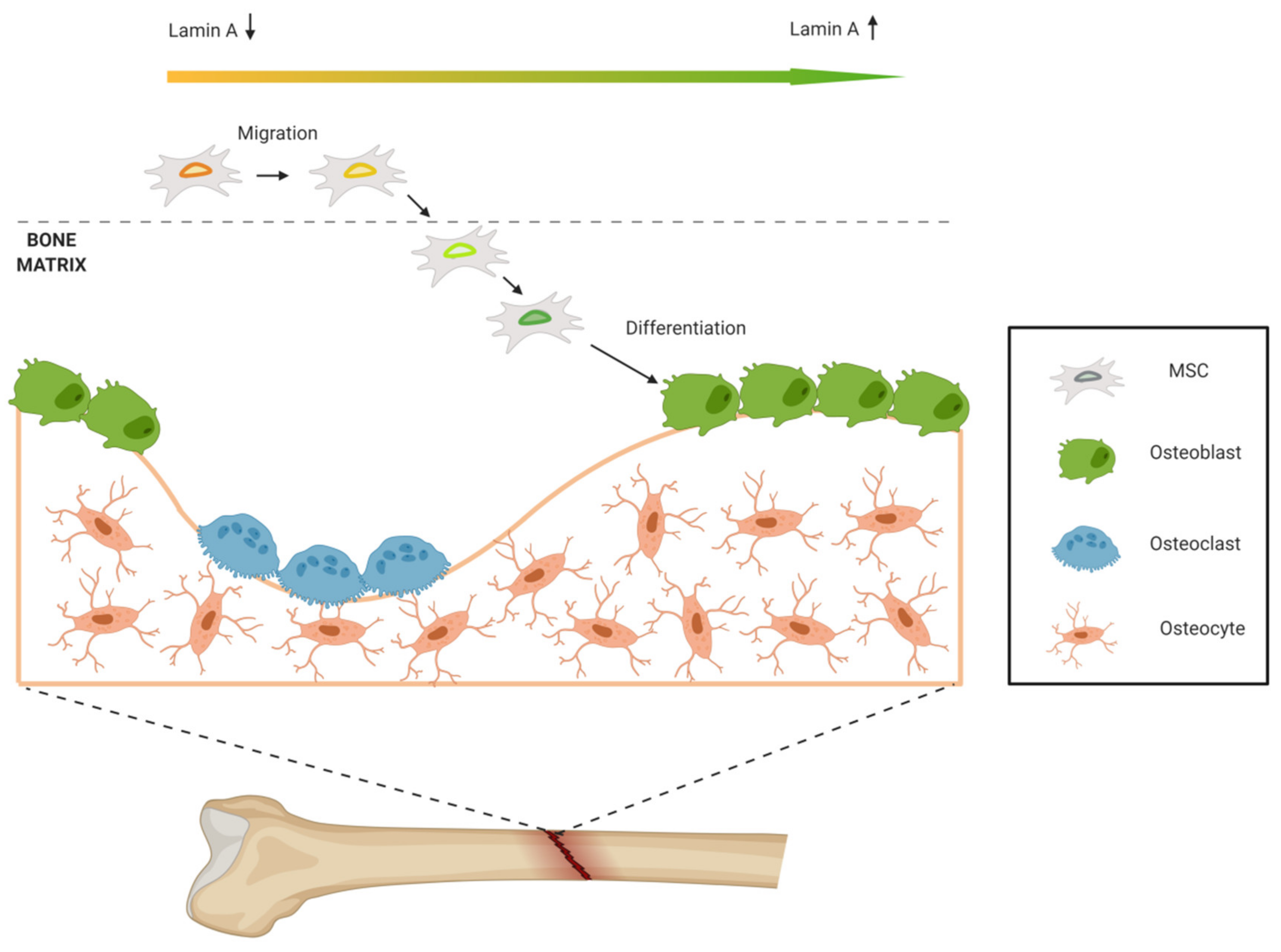
Machiels et al 1996 a type lamins are absent in early embryonic cells but are present in. Intermediate filaments provide stability and strength to cells. The nuclear lamina is highly important for migration of both primary and cancer cells. The nuclear lamina consists of two components lamins and nuclear lamin associated membrane proteins.
The lamins are type v intermediate filaments which can be categorized as either a type lamin a c or b type lamin b 1 b 2 according to homology of their dna sequences biochemical properties and cellular localization during the cell cycle. The lmnb1 gene provides instructions for making the lamin b1 protein. Lamin b1 is a structural protein called an intermediate filament protein. This adipocyte nuclear lamina repertoire contrasts with other cells such as skeletal muscle and cardiomyocytes where lamin b2 is the prevalent b type lamin and lamin b1 is absent.
Lamin b1 is a scaffolding supporting component of the nuclear envelope which is the structure that surrounds the nucleus in cells. Laminin is defined by the webster medical dictionary as a glycoprotein that is a component of connective tissue basement membrane and that promotes cell adhesion in other words looking at laminin as a kind of glue isn t far from the truth.