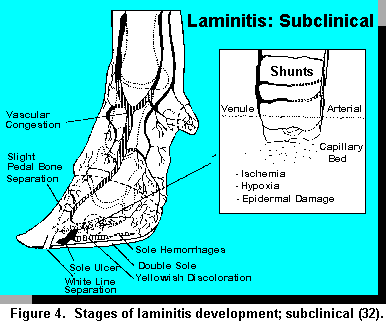
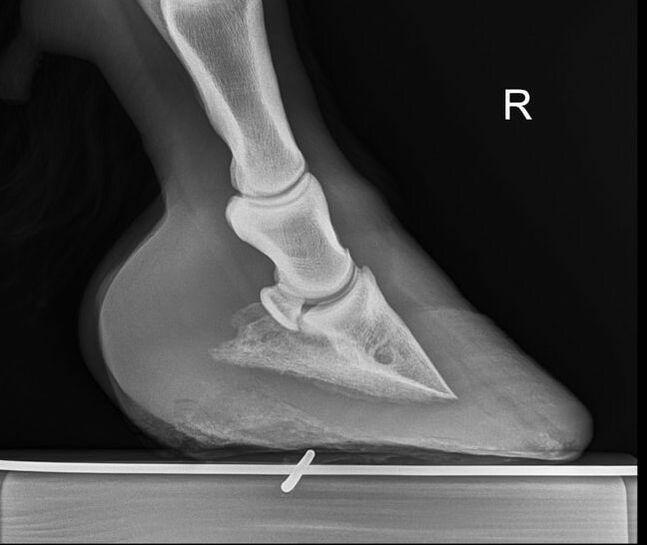
Laminitis Symptoms In Sheep

There are no definitive clinical signs of subclinical laminitis.
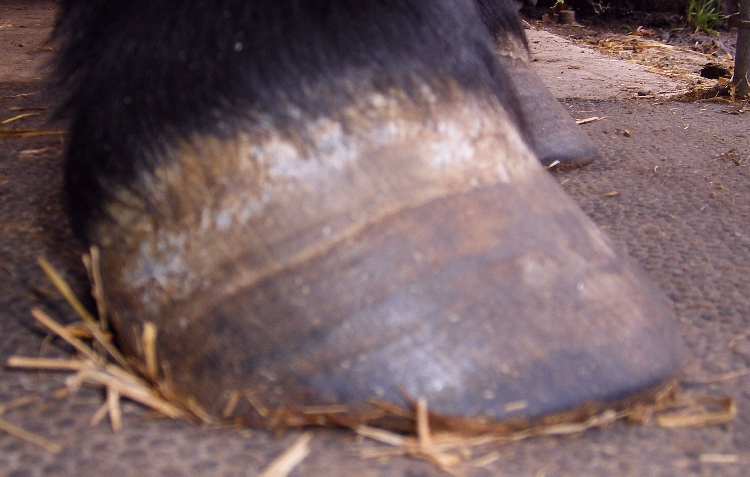
Laminitis symptoms in sheep. If your horse is suddenly more sensitive when putting pressure on their hoof with hoof testers they may be having an onset symptom of laminitis. June 24 2018 01 22 45 pm no shep the x rays were only of the ankle and knee joints but he examined her well and found nothing that indicated arthritis in any joint no clicking etc thanks for your interest. By overgrowth of the hoof. Rings in hoof wall that become wider as they are followed from toe to heel.
Sometimes infection is enhanced by impaction with sand mud or feces. A hoof that is suffering from the start of laminitis will feel warmer when touched. However in any group of cows presented with the same set of insults a few cows may show slight signs of the subacute form of the disorder. Especially up around the coronary band.
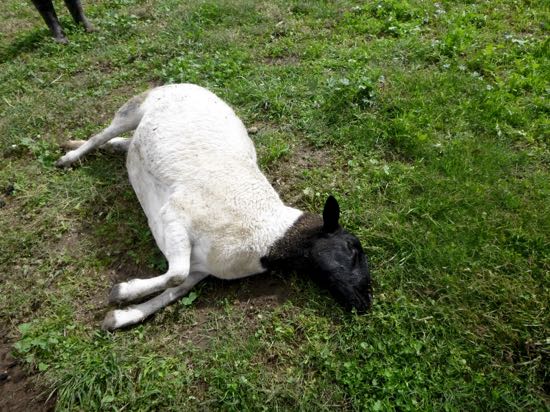
Symptoms of laminitis disease in sheep and goats laminitis disease क लक षण न म ल ख त ह 1 laminitis disease भ ड य बकर नक ख र hoof स सम ब ध त ह त ह 2 भ ड बकर य क laminitis disease म अपन ख र क तलव म. If the sheep is persistently lame the kindest and correct thing to do is to send her off she could likely have a joint issue or maybe have damaged some cartilage running or have had a foot infection in the winter which has damaged the joint which she will not likely recover from. Forefeet are affected more commonly. Inflammation will give off heat.
Lameness is severe and the affected digit may be hot and tender. Many of these symptoms can lead to lameness. Sheep might also have inflammation of the growth plates and joints. Goats may appear anxious and uncomfortable and grind their teeth from pain.
Laminitis the separation or failure of laminae which connect the hoof wall to the coffin bone within can cause permanent structural changes in a horse s foot leading to repeated bouts of disease. Signs of chronic laminitis may include the following. Some cows with subacute laminitis may walk in a deliberate careful manner with the legs carried beneath the animal when walking. Or by separation of the wall after laminitis.
There is usually a vague lameness at first and or an increasing tendency for the goats to walk on their knees. Hoof abscesses cracks and hoof overgrowth can appear in the case of chronic laminitis.