Laminitis Symptoms In Cattle

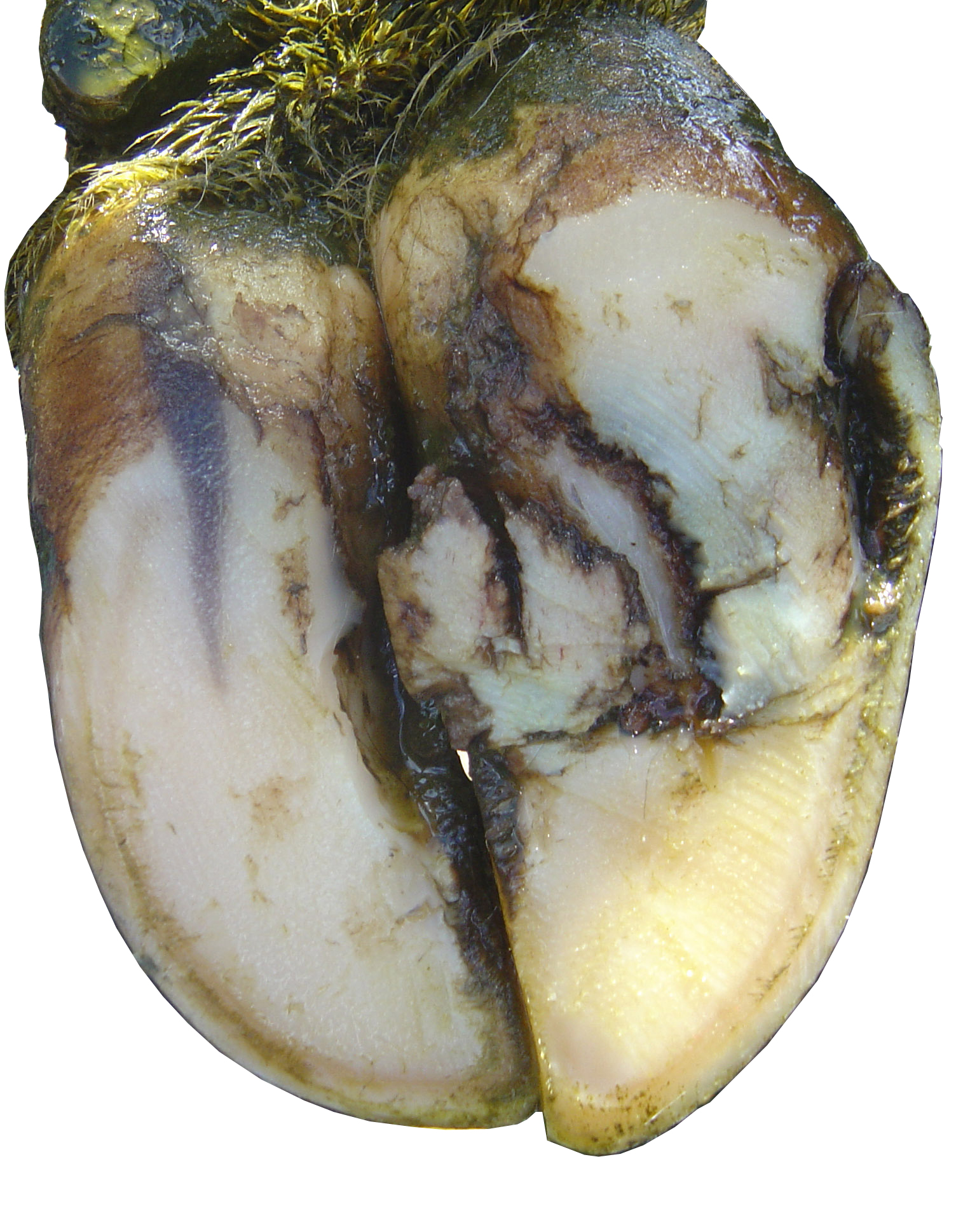
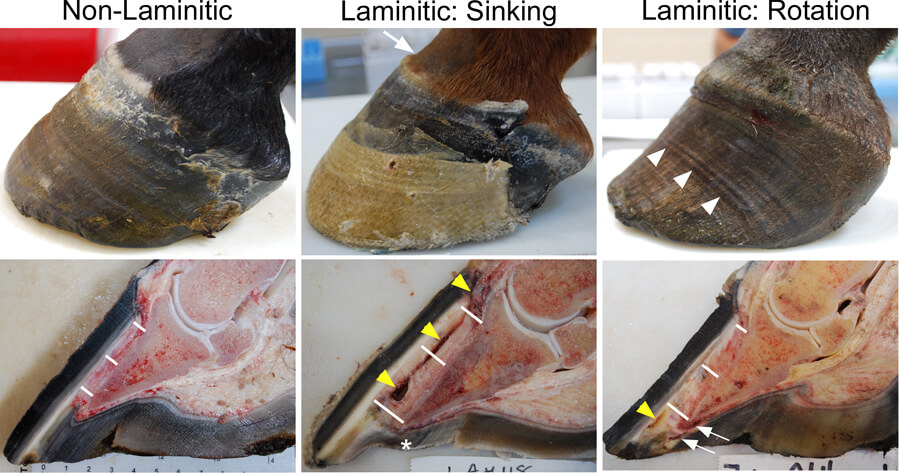
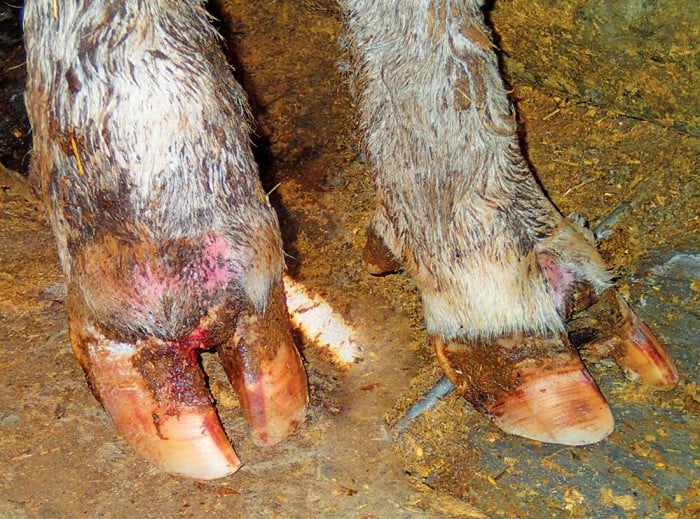
In chronic laminitis the shape of the claws is altered.
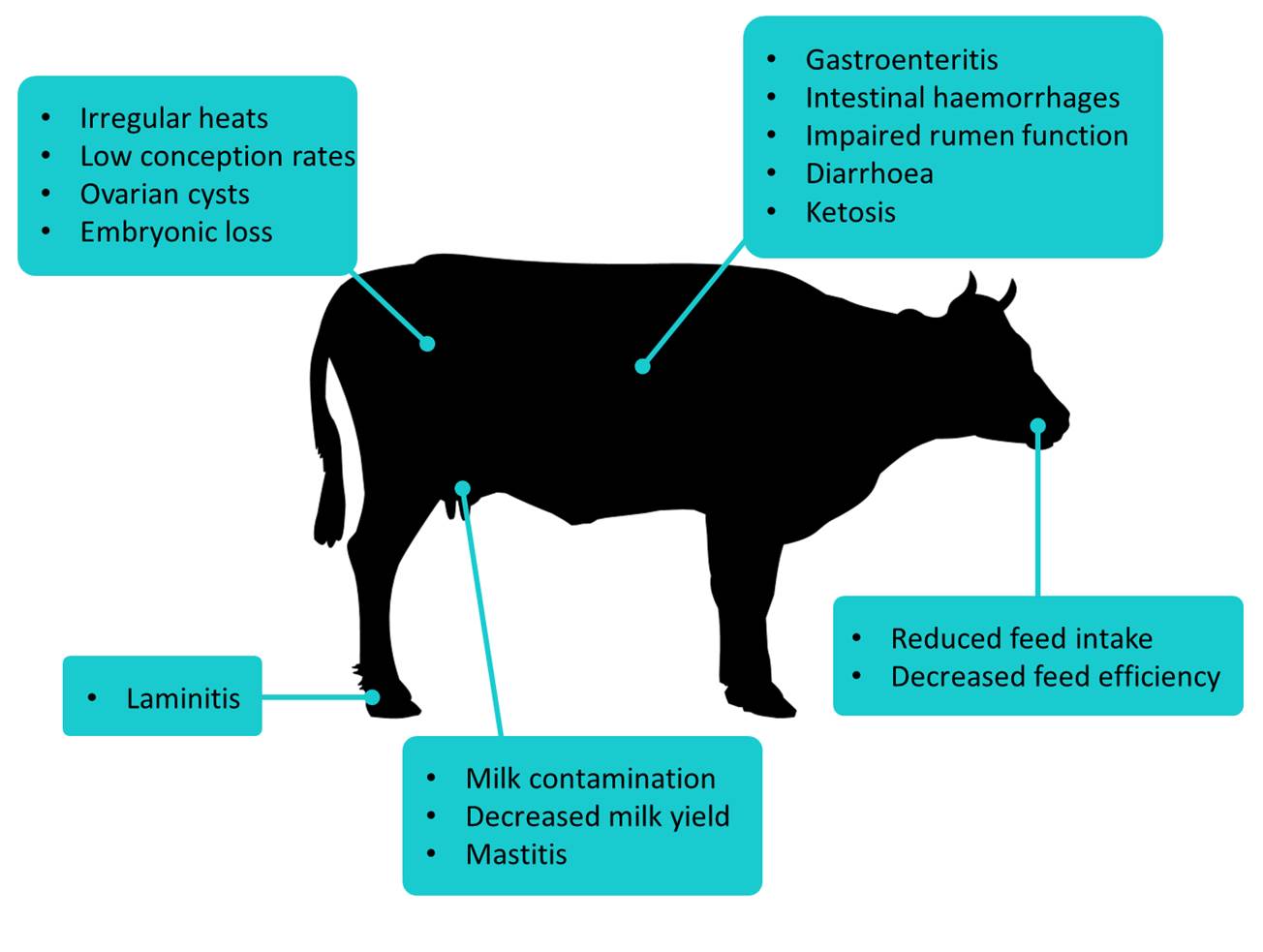
Laminitis symptoms in cattle. The sole horn reveals red and yellowish discolourations within five days. There are no definitive clinical signs of subclinical laminitis. Cattle with chronic laminitis slipper foot usually have overgrown disfigured hooves. Clinical signs can be seen in calves fed too high of a concentrate diet at 6 months of age this opens the door for more severe laminitis as the animal grows older.
Nsaid non steroidal anti inflammatory drug injectable ketoprofen 2 to 4 mg kg im iv. Some cows with subacute laminitis may walk in a deliberate careful manner with the legs carried beneath the animal when walking. Bruised soles or stone bruises widened white line commonly called seedy toe with occurrence of seromas blood pockets and or abscesses. Affected cattle walk softly with.
Injectable diphenhydramine 0 5 to 1 0 mg kg iv im. Laminitis is more common and more important than it is usually given credit for. Prominent clinical signs of acute laminitis are a tender gait and arched back. Antihistamines may be useful e g.
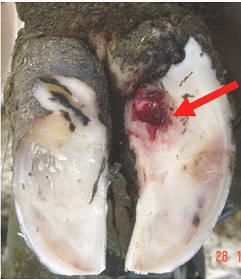
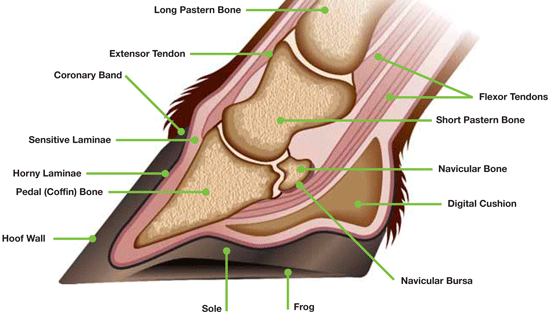
Some cows with subacute laminitis may walk in a deliberate careful manner with the legs carried beneath the animal when walking. There is some probably unnecessary disagreement over the naming of this condition since there are no laminae on the sole in cattle meaning a more accurate name would be coriitis. Heavier cattle or cattle held on feed for too long are at a higher risk for lameness. This then puts pressure on the sole and can create abscesses.
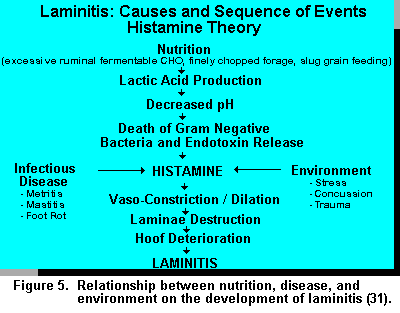
Correct grain overload keeping the animal moving and the claws cool. High grain rations erratic feed consumption due to weather factors or feed supply problems and improper feed processing are risk factors for laminitis. There are no definitive clinical signs of subclinical laminitis. Inflammation of the sensitive corium causes pressure pain and loss of cohesion between the horn and the underlying structures of.
Rings in hoof wall that become wider as they are followed from toe to heel. Signs of chronic laminitis may include the following. Never feed on 1 day enough grain for 2 3 days. However in any group of cows presented with the same set of insults a few cows may show slight signs of the subacute form of the disorder.
Cattle infected with mycoplasma bovis are at risk of joint infection. In subacute and chronic cases clinical signs are less severe. Laminitis can be caused by rumen acidosis. The coronary band is covered with a rough fringe of horn and the hoof appears rippled.
However in any group of cows presented with the same set of insults a few cows may show slight signs of the subacute form of the disorder. This might include assuring that all gates and doors that guard house stored grain are in good repair. In order to prevent laminitis do not feed excessive amounts of grain to your cattle.