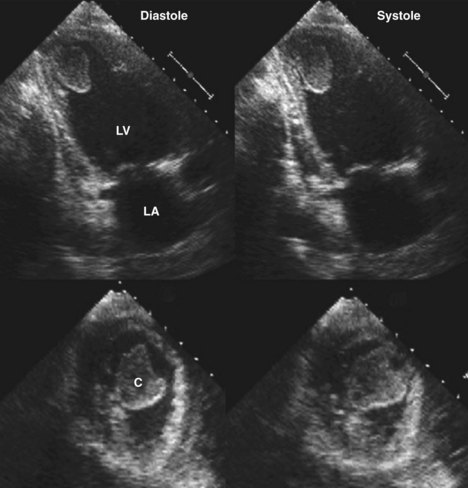
Laminated Thrombus Ventricle

Typically the clot is a mural thrombus meaning it is on the wall of the ventricle.
Laminated thrombus ventricle. Of the 231 patients with echocardiographic evidence of thrombus resolution 20 8 7 developed a stroke or systemic embolism within 30 days after the echocardiogram. The next day she col lapsed suddenly with cyanosis tachypnea and hypotension with a slow idioventricular rhythm and died within a few minutes. Studies have demonstrated high incidence of lvt following anterior myocardial infarction lvt carries both short term and long term risk of embolic events which may result in stroke and systemic complications 2 3. Lvt is a common complication of acute myocardial infarction ami.
Left ventricular thrombus is a blood clot in the left ventricle of the heart. Department of internal medicine cardiovascular division university of texas southwestern medical center dallas texas usa summary. Intracardiac thrombi are seen in a variety of clinical settings and can result in severe morbidity or even death from embolic events they can occur following myocardial infarction with ventricular thrombus formation or with atrial fibrillation and mitral stenosis where atrial thrombi predominate. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes.
It means not coded here. Contemporary epidemiologic data suggest the incidence of lv thrombus detected using optimal imaging modalities may be as high as 15 in patients with st segment elevation mi stemi and up to 25 in patients with anterior mi. Left ventricular lv thrombus is a feared complication of lv dysfunction associated with high rates of systemic embolism morbidity and mortality. The primary risk of lvt is the occurrence of cardiac embolism in which the thrombus detaches from the ventricular wall and travels through the circulation and blocks.
Traditionally lv thrombus has been associated with acute myocardial infarction mi. At autopsy she was found to have laminated thrombus in the superior vena cava right atrium and ventricle but no evidence of pulmonary embolism. Kfeley m d and l. 19 83 86 1996 reviews left ventricular mural thrombus after acute myocardial infarction ellen c.
Lv thrombus is not an uncommon complication of acute mi and is associated with systemic thromboembolism. Left ventricular mural thrombus is a well recog nized complication of acute myocardial infarction. Left ventricular mural thrombus lvt complicating myocardial infarction has significant morbidity and potential mortality. Median follow up was 351 days interquartile range iqr 51 866 days.
Thrombi in the chambers of the left heart are a common source of complications like stroke and.