Laminated Root Rot In Washington
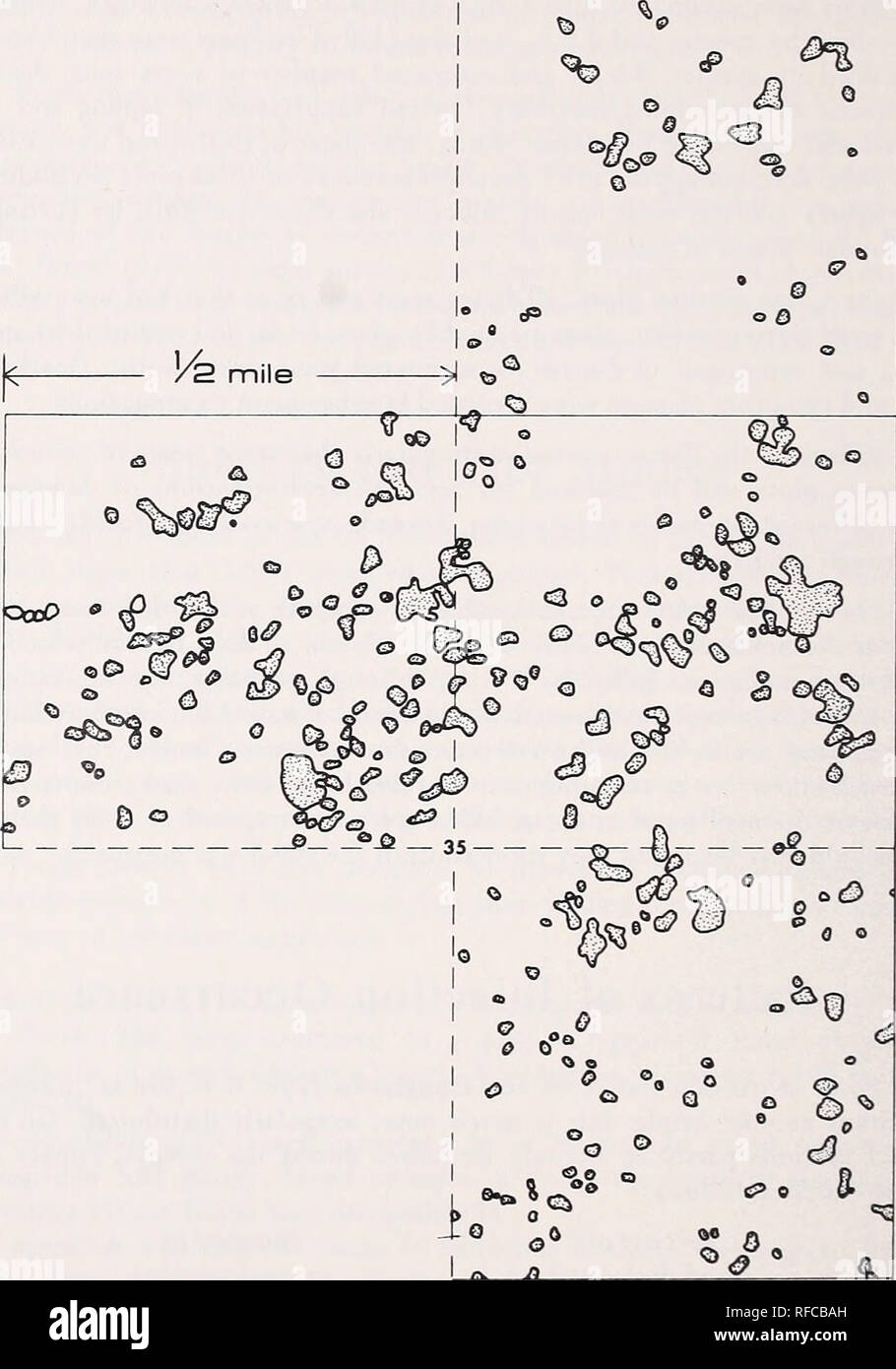
Surveys indicate approximately 5 of the area of highly susceptible host types in oregon and washington is out of production because of this disease.
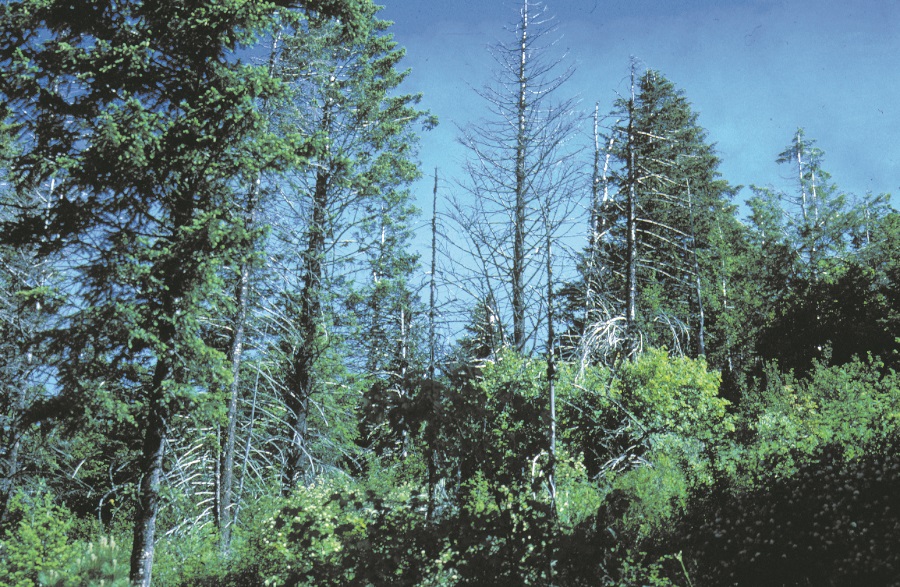
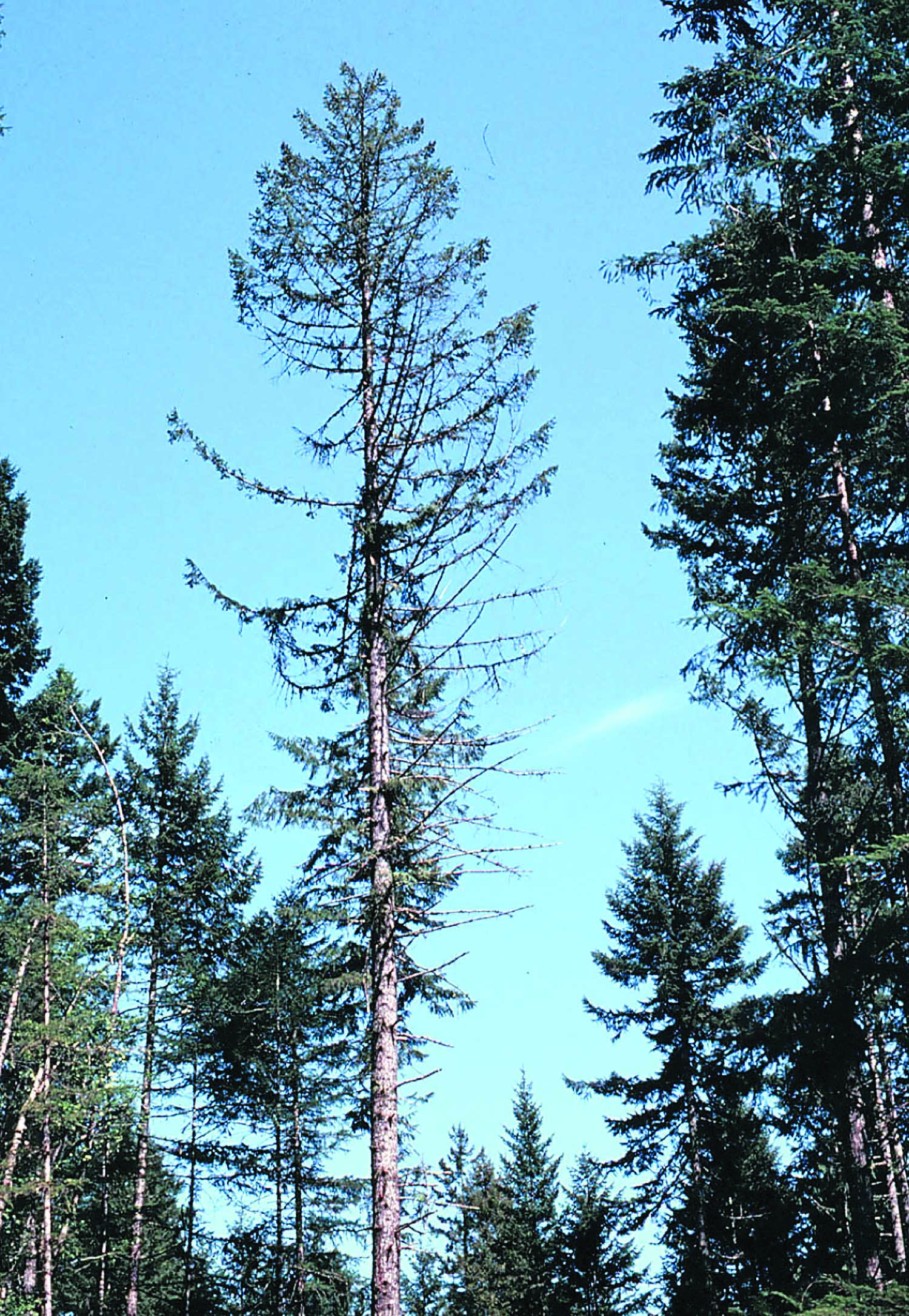
Laminated root rot in washington. Laminated root rot also known as yellow ring rot is caused by the fungal pathogen phellinus weirii laminated root rot is one of the most damaging root disease amongst conifers in northwestern america and true firs douglas fir mountain hemlock and western hemlock are highly susceptible to infection with p. Weirii a few species of plants such as western white pine and lodgepole pine are. On january 9 the washington state academy of sciences presented its special report opportunities for addressing laminated root rot caused by phellinus sulphurascens in washington s forests to commissioner of public lands peter goldmark. Keep in mind that if one of your trees becomes infected it can be passed to surrounding trees.
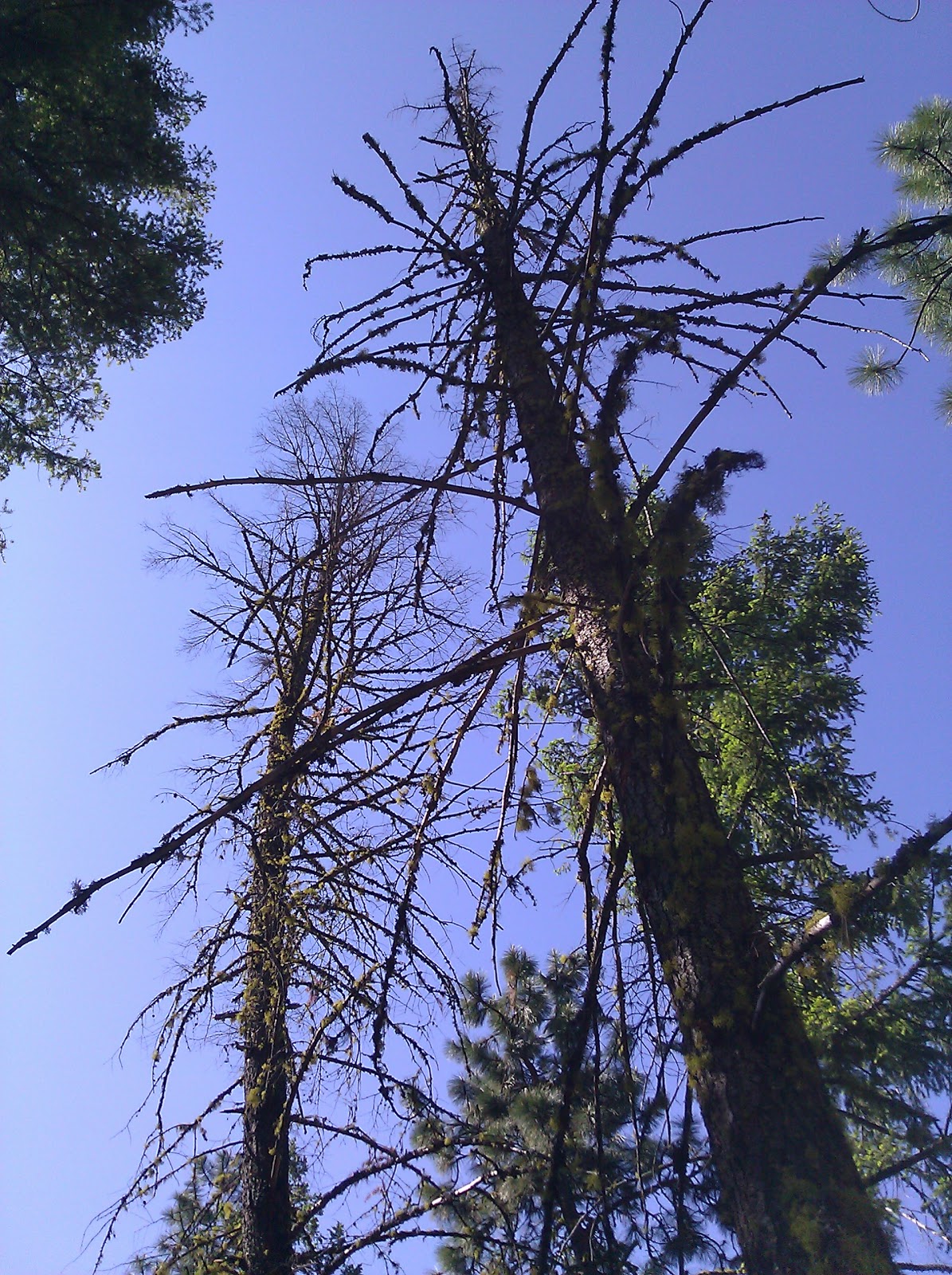
Flattened conks develop on the undersides of roots or logs. Laminated root rot laminated root rot caused by the fungus phellinus poria weirii is responsible for an annual estimated volume loss of 32 million cubic feet in the west side douglas fir type. It is estimated to cause annual losses of 32 million cubic feet of wood in western oregon and washington and may cause equally staggering losses in the eastern. Construction activity usually worsens the situation and can lead to tree failures and property loss.
Avoid building near centers of root rot infection. Laminated root rot caused by the fungus phellinus weirii is the most damaging root disease in the pacific northwest and one of the most difficult to control. Laminated root rot creates short term snags of any size and all sizes of down wood by killing or decaying the root system and butts of host trees. To help protect your trees and shrubs here s the signs to look for as well as how it spreads.
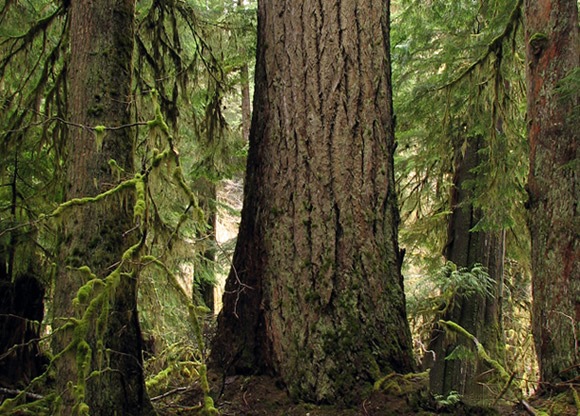
Laminated root rot coniferiporia sulphurascens key wildlife value. Consensus to focus on laminated root rot of douglas fir the committee chose lrr as the root disease of washington forests and more specifically. It can create trees with hollow butts which may continue to provide habitat when they fall. The academy was formed in 2005 and is comprised of washington s leading scientists and engineers.
















