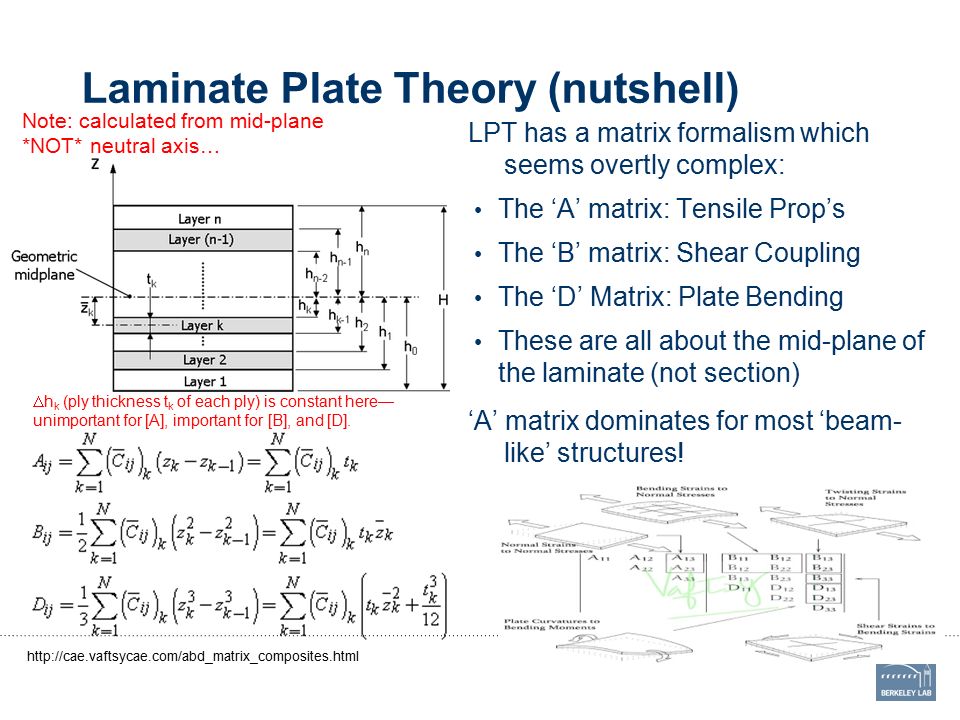
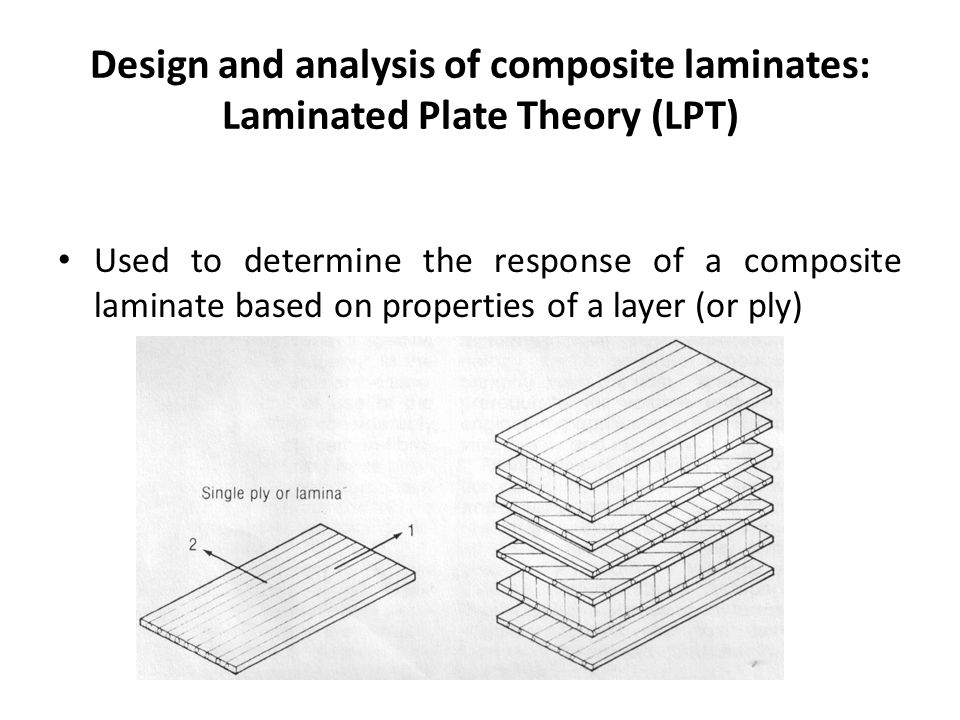
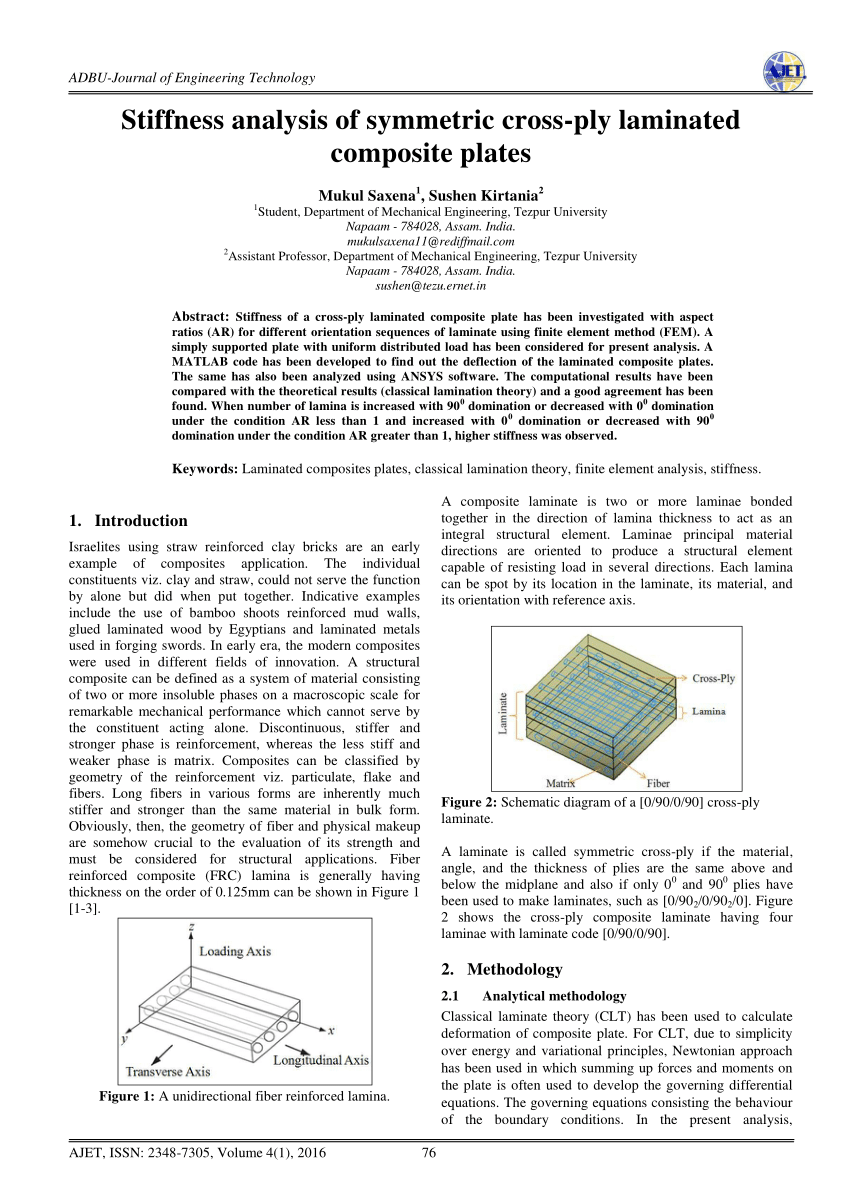
Laminated Plate Theory

Thin plate classical laminate model.
Laminated plate theory. Classical lamination theory clt is a commonly used predictive tool which evolved in the 1960s which makes it possible to analyze complex coupling effects that may occur in composite laminates. In contrast to homogeneous isotropic plates heterogeneity of the anisotropic structure of laminated composite plates often leads to the appearance of imperfections in the. Determination of stress strain state in contemporary laminated composite plates containing layers with continuous unidirectional fibers requires the application of refined plate theories which include layerwise theory. 7 2 thin laminated plate theory consider a rectangular thin laminated composite plate of length a width b and thickness h as shown in fig 7 1.
The plate consists of a laminate having n number of laminae with different materials fibre orientations and thicknesses. Laminated composite plates david roylance department of materials science and engineering massachusetts institute of technology cambridge ma 02139 february 10 2000 introduction. Classical theory of plates is applicable to very thin and moderately thin plates while higher order theories for thick plates are useful. Theory of plates and shells mcgraw hill new york 1959.
The four cornerstones of the lamination theory are the kinematic constitutive force resultant and equilibrium equations. Many references are available where classical lamination theory is utilized to describe composite material behavior. The stack is defined by the fiber directions of each ply like this. Classical laminate theory has been extensively used to describe the behavior of composite materials under mechanical thermal and hygothermal loading conditions.
A summary of classical lamination theory defining the laminate a laminate is an organized stack of uni directional composite plies uni directional meaning the plies have a single fiber direction rather than a weave pattern. The classical plate theory usually assumes that the material is isotropic while a fiber reinforced composite laminate with multiple layers plies may have more complicated stress strain relations. Basic mechanics of laminated composite plates the mechanics of laminated composite materials is presented in a clear manner with only essential derivations included. The constitutive equations in all of their forms are developed and then summarized in a separate section.
It is able to predict strains displacements and curvatures that develop in a laminate as it is mechanically and thermally loaded.