Laminated Plate Theory Definition

In a laminate plate individual continuous fiber matrix laminas are oriented in the required directions and bonded together.
Laminated plate theory definition. 3 3 1 classical laminated plate theory the clpt is an application to composite plates of the classical thin plate theory originally developed for homogeneous plates. 4 8e9 enter ply thickness. 230e9 enter modulus in transverse direction. The stack is defined by the fiber directions of each ply like this.
Classical lamination theory clt is a commonly used predictive tool which evolved in the 1960s which makes it possible to analyze complex coupling effects that may occur in composite laminates. In continuum mechanics plate theories are mathematical descriptions of the mechanics of flat plates that draws on the theory of beams. 6 6e9 enter principal poisson ratio. 25 enter shear modulus.
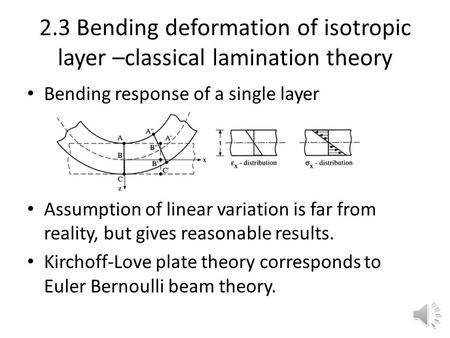
Plate assign properties for lamina type 1. In materials science a composite laminate is an assembly of layers of fibrous composite materials which can be joined to provide required engineering properties including in plane stiffness bending stiffness strength and coefficient of thermal expansion. Plates are defined as plane structural elements with a small thickness compared to the planar dimensions 1 the typical thickness to width ratio of a plate structure is less than 0 1 citation needed a plate. The classical lamination theory is almost identical to the classical plate theory the only difference is in the material properties stress strain relations.
The classical plate theory usually assumes that the material is isotropic while a fiber reinforced composite laminate with multiple layers plies may have more complicated stress strain relations. It can be axiomatically formulated based on the following a priori assumptions. Design tools eindhoven university of technology 1 linear plate bending a plate is a body of which the material is located in a small region around a surface in the three dimensional space. Enter 1 to stop.
It is able to predict strains displacements and curvatures that develop in a laminate as it is mechanically and thermally loaded. A laminate is an organized stack of uni directional composite plies uni directional meaning the plies have a single fiber direction rather than a weave pattern.