Laminated Left Ventricular Thrombus
Identification of left ventricular mural thrombus lvt may be challenging depending on the imaging modality used.
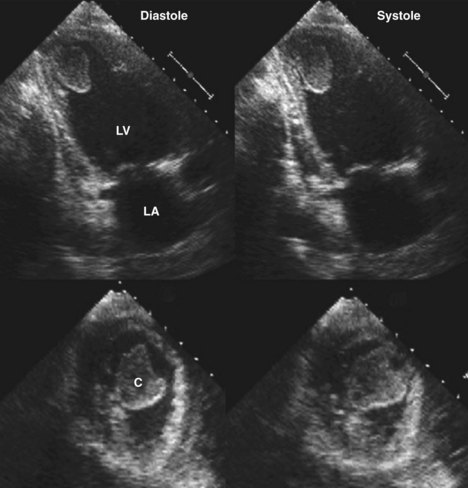
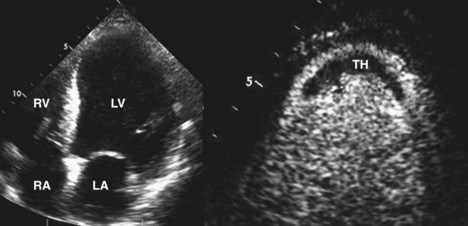
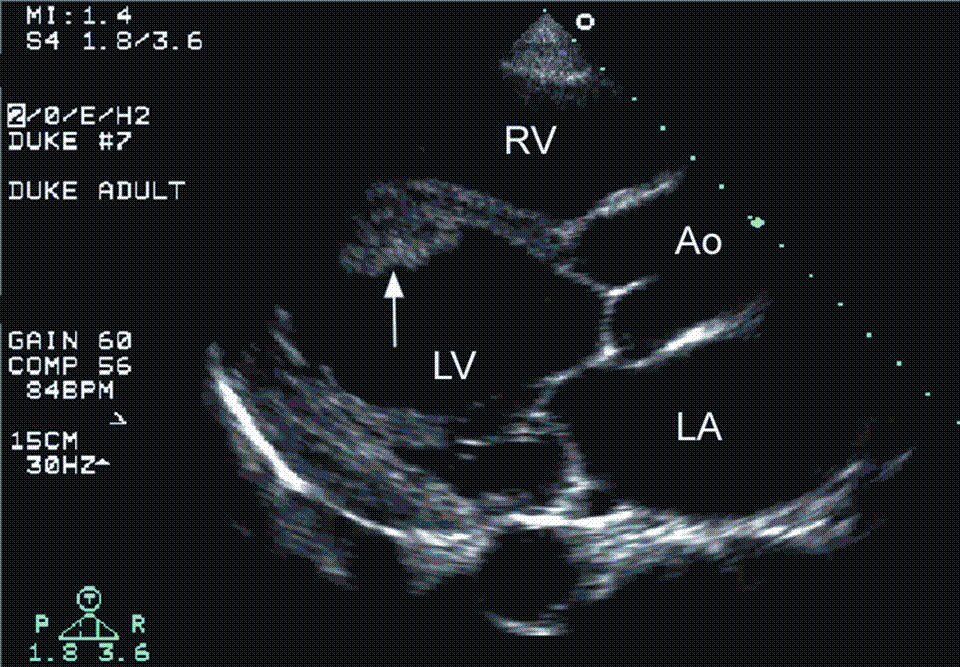
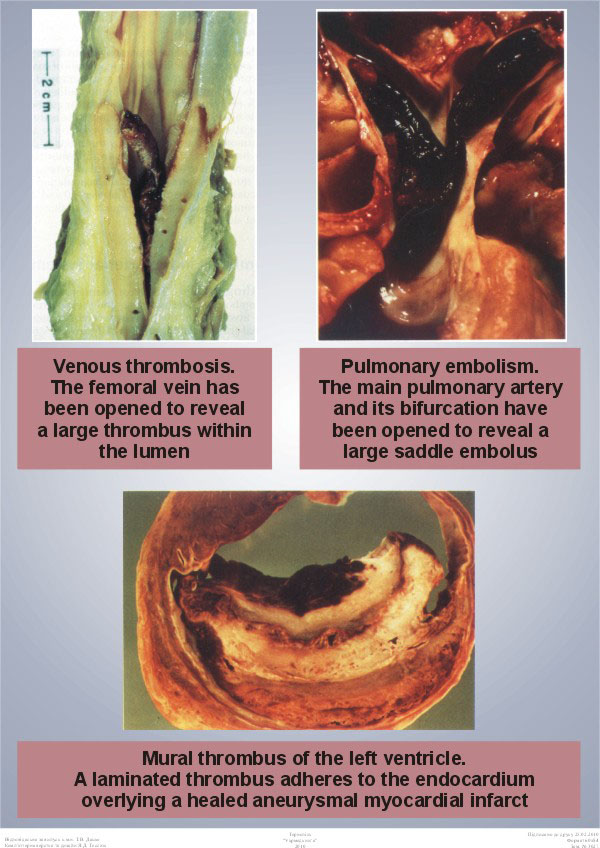
Laminated left ventricular thrombus. Left ventricular thrombus lvt complicates both ischemic and non ischemic cardiomyopathies and is a potential cause of thromboembolic complications such as stroke. Acute procedural outcomes complications and clinical outcomes at 1 year were assessed. Appropriate detection and monitoring when thrombus is suspected is critical in surgical planning and in avoiding catastrophic patient outcomes. Typically the clot is a mural thrombus meaning it is on the wall of the ventricle.
Left ventricular thrombus is a blood clot thrombus in the left ventricle of the heart. Left ventricular thrombus formation after myocardial infarction. Traditionally lv thrombus has been associated with acute myocardial infarction mi. A calcified lvt was defined as a persistent left ventricular mural thrombus encapsulated by thickened and calcified endocardium.
Left ventricular characteristics including left ventricular ejection fraction lvef left ventricular volume wall motion cardiac output and potential mechanical complications were also collected. A sixty four years old female presented with worsening dyspnea on exertion with troponin elevation. Lvt is a common complication of acute myocardial infarction ami. Left ventricular lv mural thrombus is a well recognized complication of acute myocardial infarction.
Patients with laminated lv thrombus on transthoracic echocardiogram who underwent scar mediated vt ablation at two centers from 2010 to 2013 were retrospectively analyzed. All patients had failed medical therapy. Left ventricular lv thrombus is a feared complication of lv dysfunction associated with high rates of systemic embolism morbidity and mortality. We present a case of lvt which was incidentally identified on cine cardiac magnetic resonance imaging cmr.