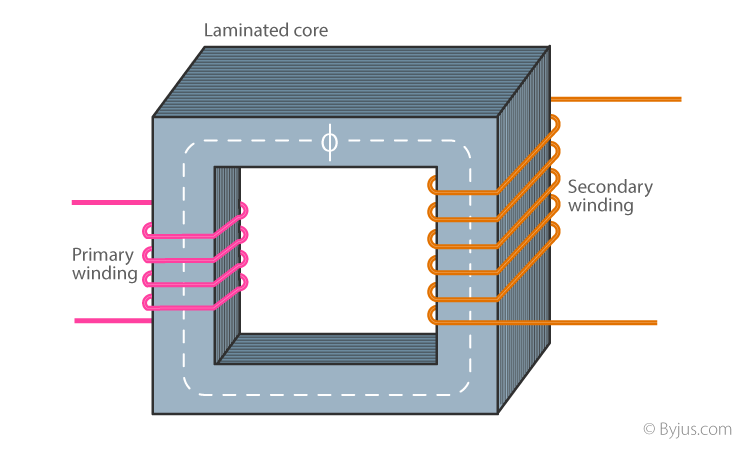
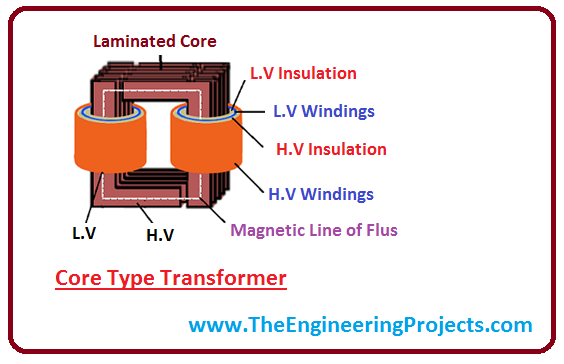
Laminated Core Transformer Definition

These two types are distinguished from each other by the manner in which the primary and secondary coils are place around the steel core.
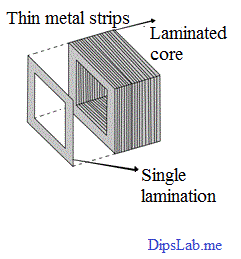
Laminated core transformer definition. Reduce all above losses. Laminations may be cut to their finished shape by a punch and die. Laminated means made up of insulated layers of iron glued together rather than being in a single solid lump. Construction of an inductor using two er cores a plastic bobbin and two clips.
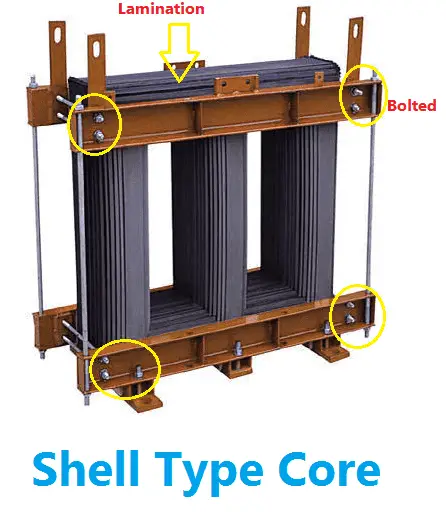
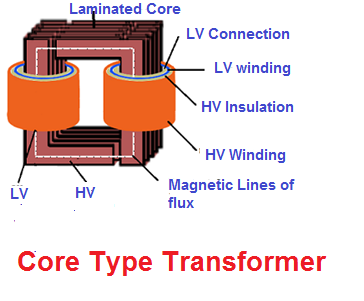
This type of core is frequently used for power transformers autotransformers and inductors. This implementation of faraday s law of induction is valuable because the ratio of input to output voltages and currents can be set by adjusting the ratio of primary turns to secondary turns. Transformers generally have one of two types of cores. The purpose of providing an iron core in a transformer is to.
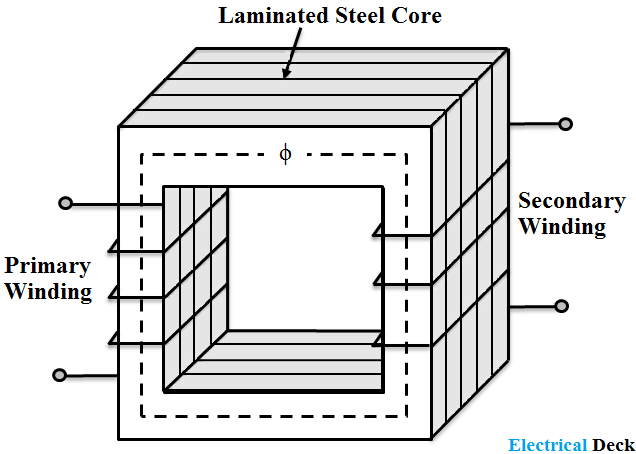
Transformer core laminations are usually stacked alternately to each other to produce an overlapping joint with more lamination pairs being added to make up the correct core thickness. It therefore does not get such big a currents induced in it. A transformer is a passive electrical device that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another or multiple circuits. Comment related questions on transformers.
Reduce eddy current losses. A transformer core is laminated to. Core type and shell type. A transformer comprises a primary and a secondary coil that are electromagnetically linked.
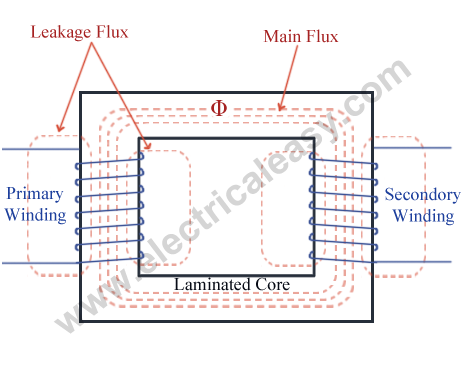
This means that alternating current passed through the primary creates a varying magnetic field around it which in turn induces an alternating current in the secondary. A laminated core has a higher resistance than a non laminated one with the same number of domains. This alternate stacking of the laminations also gives the transformer the advantage of reduced flux leakage and iron losses. A varying current in any one coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer s core which induces a varying electromotive force across any other coils wound around the same core.
Electrical steel is an iron alloy tailored to produce specific magnetic properties. Core type with this type the windings surround the laminated core. These strips are cut to shape to make laminations which are stacked together to form the laminated cores of transformers and the stator and rotor of electric motors. Small hysteresis area resulting in low power loss per cycle low core loss and high permeability.