Laminate Failure Theory

9 mccartney 1998 2002 employed an analysis based on damage mechanics.
Laminate failure theory. The proposed failure analysis methodology was used to simulate the nonlinear laminate behavior and progressive damage of selected laminates under both uniaxial and biaxial load conditions up to. Does anybody know how to set the solution for this output vector 6060 laminate max failure index in previous version femap 11 1 2. In femap 11 1 2 miss this output. A summary of classical lamination theory defining the laminate a laminate is an organized stack of uni directional composite plies uni directional meaning the plies have a single fiber direction rather than a weave pattern.
It was shown to have the same form as that for three dimensionally isotropic materials when in the 2 d state of plane stress. Strength of a composite laminate is based on the strength of the individual plies within the laminate. The theory employs a form of interactive failure criterion at the fibre and matrix constituent level and it uses a finite element method to calculate values of stress at the laminate level. 1 christensen and lonkar derived the failure criterion for quasi isotropic laminates.
Orthotropic laminates failure theory in ref. Hi i have the same problem. The tsai wu failure criterion is a phenomenological material failure theory which is widely used for anisotropic composite materials which have different strengths in tension and compression. As the load is applied to the laminate there will be a first ply failure followed by other ply failures until the last ply fails which would be the ultimate failure.
The puck theory of failure in laminates in the guideline vdi 2014 part 3 a large part about 50 pages of the guideline vdi06 is dedicated to the laminate failure theory of puck. It is given by. The basic concept of the micro mechanics of failure mmf theory is to perform a hierarchy of micromechanical analyses starting from mechanical behavior of constituents the fiber the matrix and the interface then going on to the mechanical behavior of a ply of a laminate and eventually of an entire structure. This failure criterion is a specialization of the general quadratic failure criterion proposed by gol denblat and.
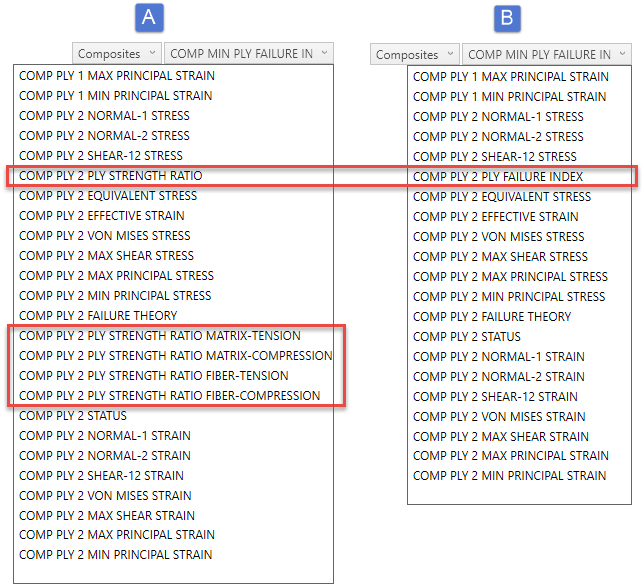
6060 laminate max failure index. The tsai wu criterion predicts failure when the failure index in a laminate reaches 1. There is still considerable uncertainty among designers on how to assess the confusing amount of failure theories and degradation models for frp. Classical lamination theory clt is a commonly used predictive tool which evolved in the 1960s which makes it possible to analyze complex coupling effects that may occur in composite laminates.
The stack is defined by the fiber directions of each ply like this. It is able to predict strains displacements and curvatures that develop in a laminate as it is mechanically and thermally loaded.