Lamin Tail Domain
Lamin tail domain containing protein 1.
Lamin tail domain. Lamin a related sequence 1. Intermediate filament tail domain containing protein 1 gene names i. 617254 lamin tail domain containing protein 1. A conserved lamin specific ig fold domain comprising residues 436 545 in human lamin a and residues 438 545 in human lamin b1.
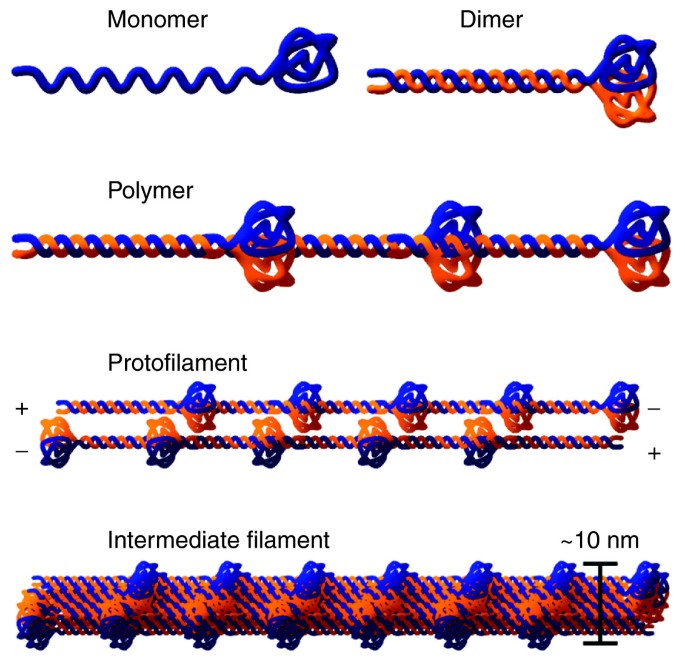
Homo sapiens human taxonomic identifier i. While the head domain of lamins is fairly consistent the composition of the tail domain varies based on the type of lamin. Similar to other if proteins lamins self assemble into more complex structures. The basic unit of these structures is a coiled coil dimer.
A t 1 publication. Pas1 candidate 1 mouse homolog of. Intermediate filament tail domain containing protein 1. Lamin tail domain containing protein 1.
Invertebrate cytoplasmic ifs share sequence similarity with nuclear lamins and also contain a c terminal tail domain with homology to the ltd 1 2 3. Natural variant i var 027732. 1 2 lamin a molecular structure and the hgps δ50 mutation. Lamins exhibit a highly conserved globular c terminal lamin tail domain ltd which has the immunoglobulin ig fold see pdoc50835.
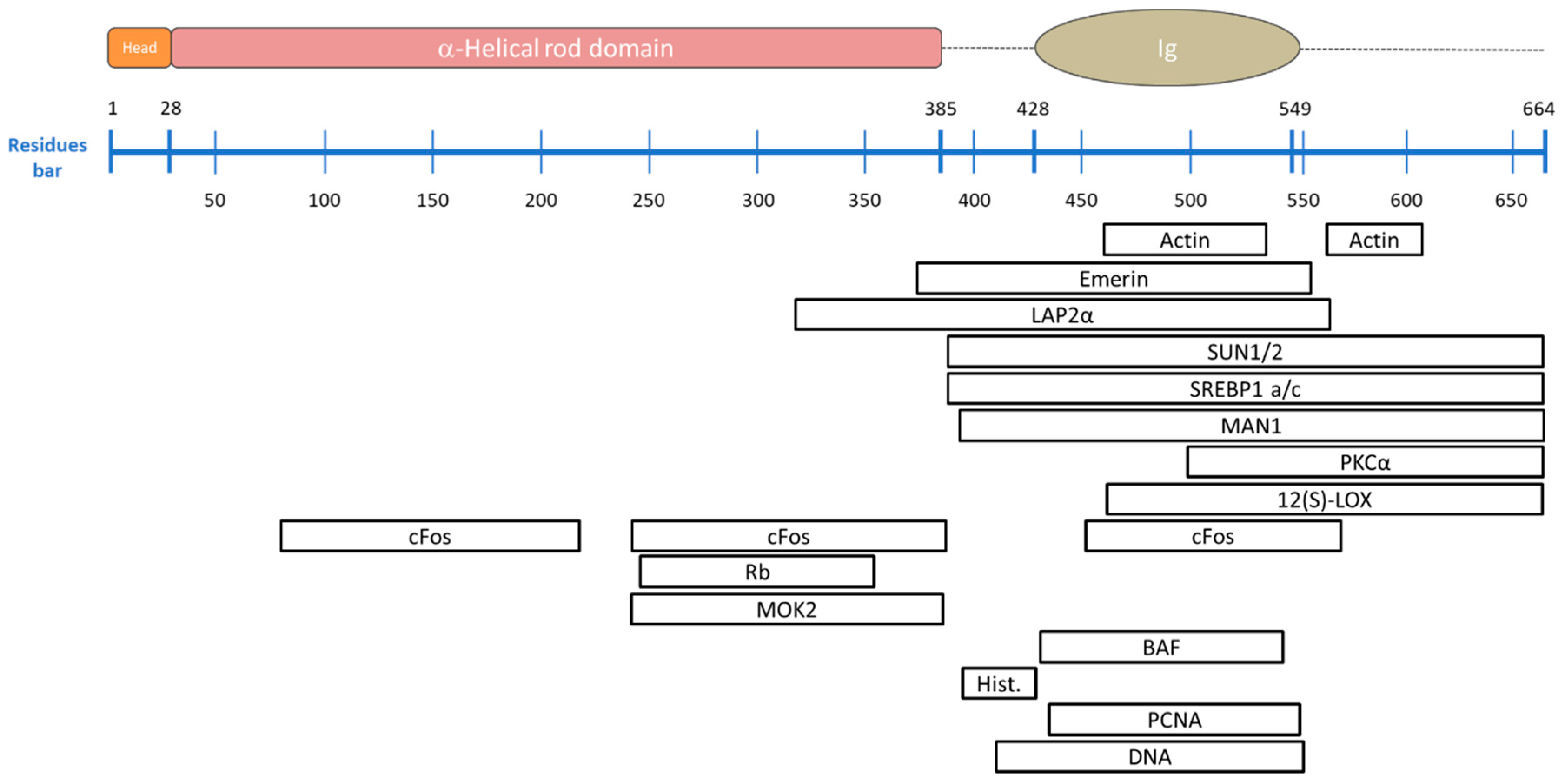
Lamin polypeptides have three major domains. 4 within the tail is one known structural feature. A small n terminal globular head long coiled coil rod and large c terminal globular tail. The specific displacement of the lamin tail domain from chromosomes by histones h2a and h2b is not an artifactual result of a change in chromatin structure caused by binding by these histones because lamin can bind specifically to polynucleosomes and nucleosome core particles could efficiently displace the binding of lamin tail to chromosomes.
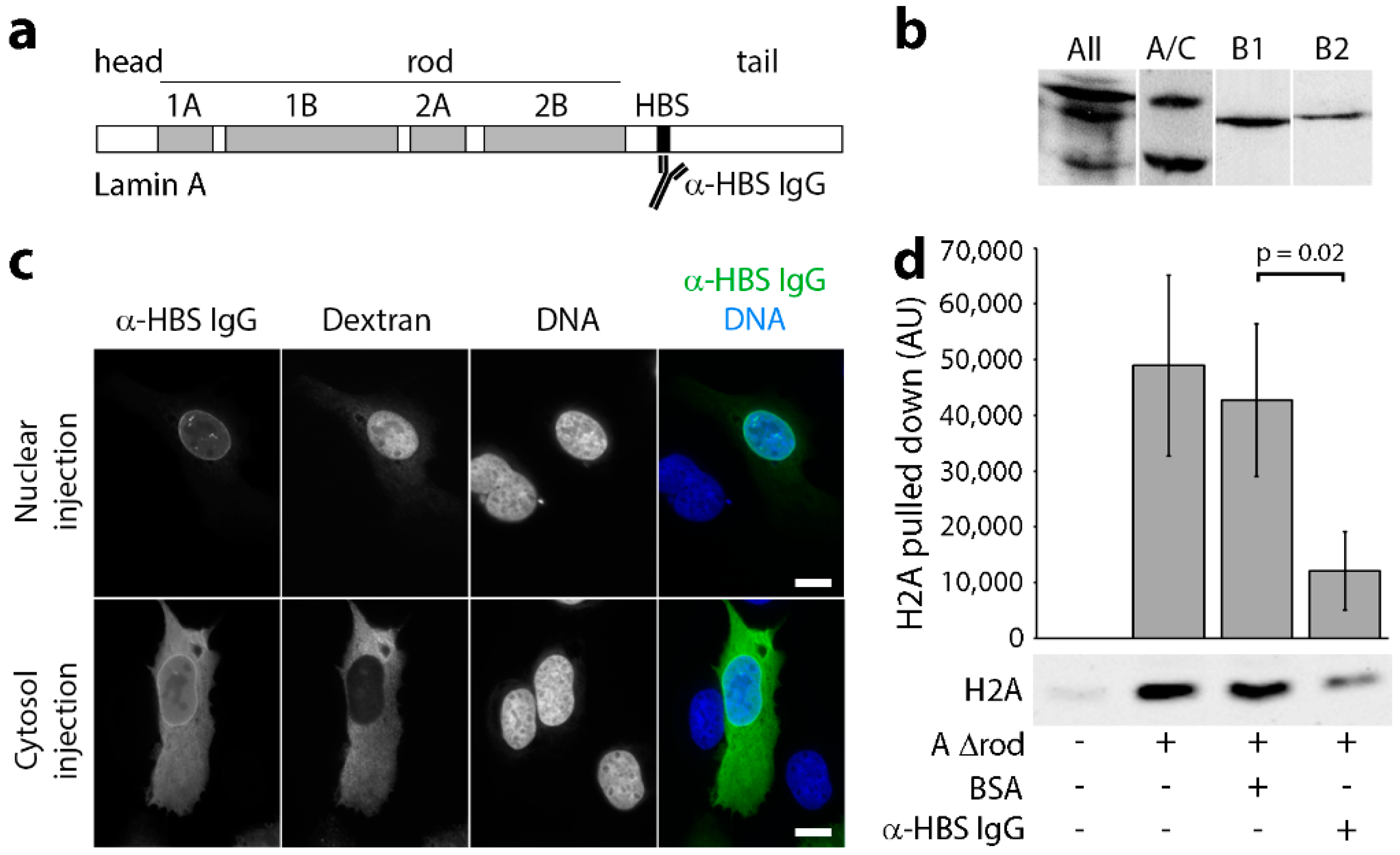
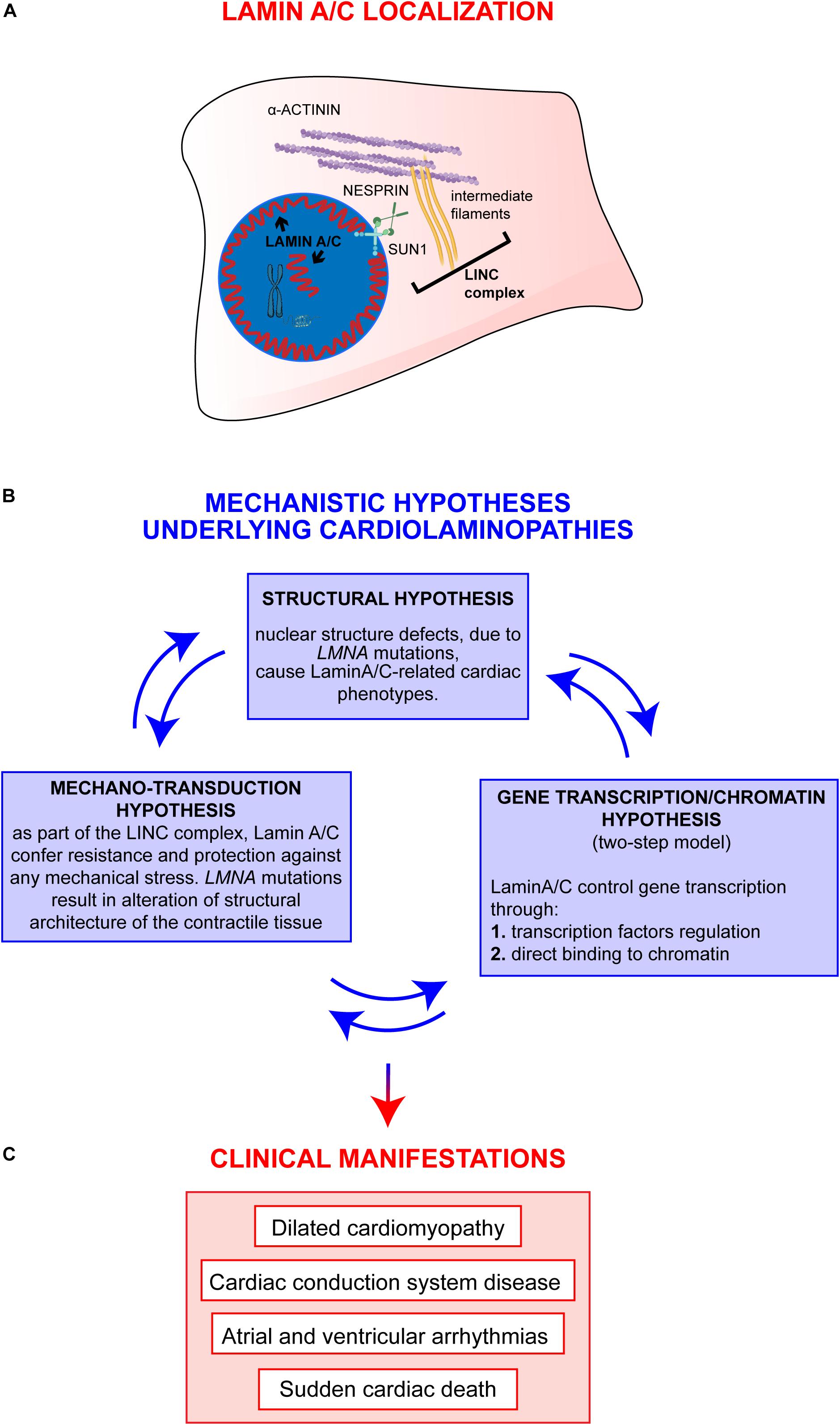
However all c terminal domains contain a nuclear localization sequence nls. Corresponds to variant dbsnp rs2061586. Taxonomic lineage i eukaryota metazoa chordata craniata vertebrata. Conduction system disease is a common feature of emery dreifuss muscular dystrophy caused by defects in the head or tail domain of the lamin gene or by emerin mutations.
Lamin a is a characteristic type v if protein that contains a globular n terminal head a segmented coiled coil α helical rod domain and a c terminal tail containing an immunoglobulin ig fold herrmann et al 2007 lamin proteins are unique from other ifs as they feature an exceptionally long c terminal tail domain herrmann et. Lamin tail domain containing protei. 25 26 the ig fold appears to mediate many specific.