Lamin Gene Expression

Keywords ptm i acetylation disulfide bond isopeptide bond lipoprotein methylation.
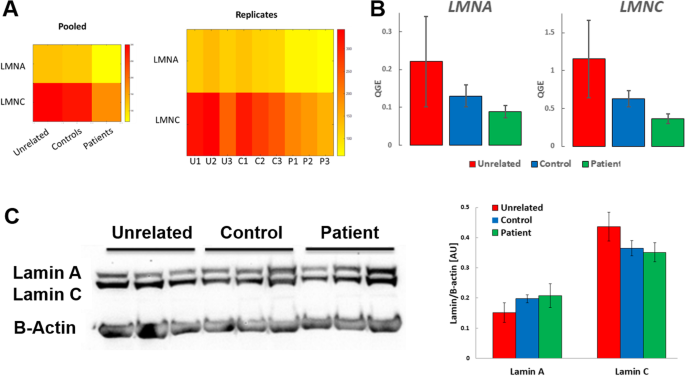
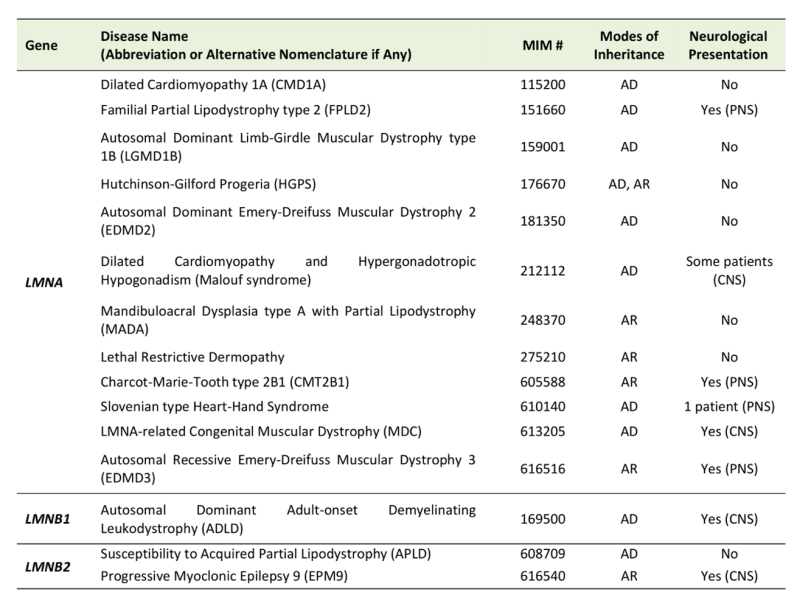
Lamin gene expression. Because lmna mutations are a common cause of inherited dilated cardiomyopathy we examined gene. Ensg00000113368 expressed in ventricular zone and 184 other tissues. This gene encodes one of the two b type proteins b1. 16 mutations in the gene encoding lamin a c cause a variety of diseases including cardiac and skeletal muscle disease.
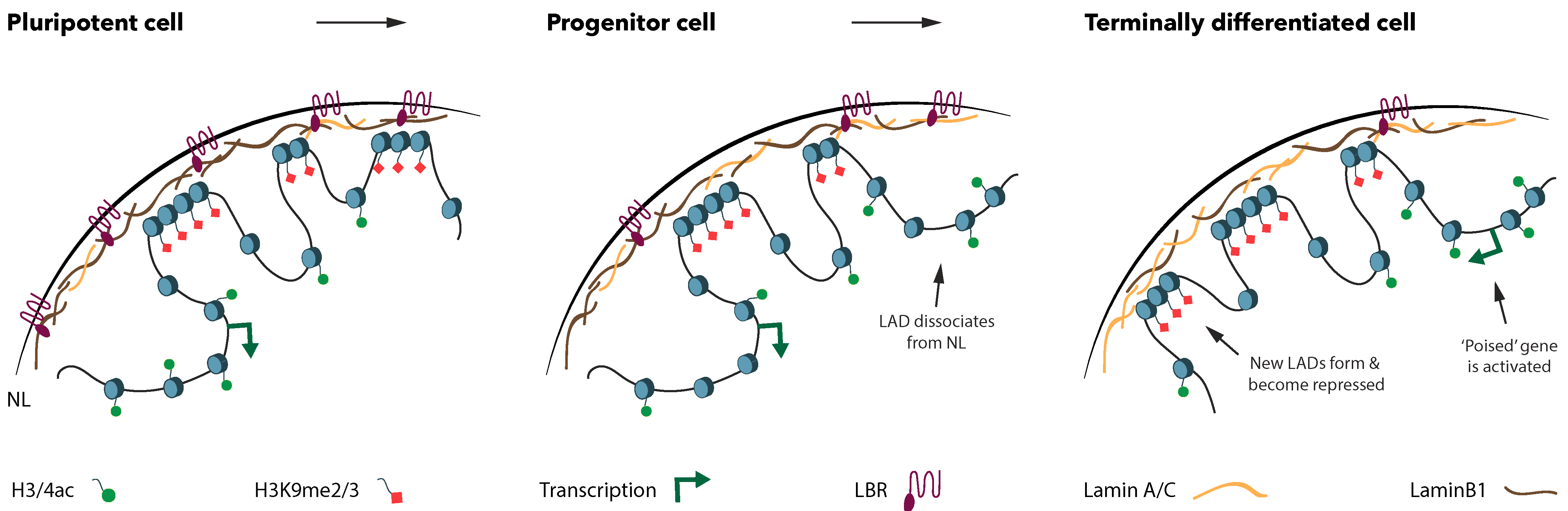
Lamin b along with heterochromatin is anchored to the inner surface of the nuclear membrane by the lamin b receptor. In addition an abnormal nuclear morphology was apparent when cultured cells overexpressed this protein. Defects in lamin b1 expression have been shown to affect the interphase chromosome position and gene expression malhas et al 2007. In addition loss of lamin a c expression has been observed in several cancers including breast cancer and it has been found that lamin a c suppression may.
Vertebrate lamins consist of two types a and b. The use of this gene expression has been cited in the following citations. Lmna mutations alter gene expression and chromosome territories. Increased phosphorylation of the lamins occurs before envelope disintegration and probably plays a role in regulating lamin associations.
The lamin family of proteins make up the matrix and are highly conserved in evolution. During mitosis the lamina matrix is reversibly disassembled as the lamin proteins are phosphorylated. An increased expression of lamin b1 can alter regions of the chromatin that are associated with the nuclear lamina and thereby affects gene that are important for myelin formation or maintenance. The gene expression hypothesis proposes that defects in ne proteins lead to pathogenic and tissue specific alterations in gene expression and is based on recent studies proposing that a type lamins and other ne proteins form a docking platform for regulatory proteins and that some of these interactions are altered by laminopathy causing.
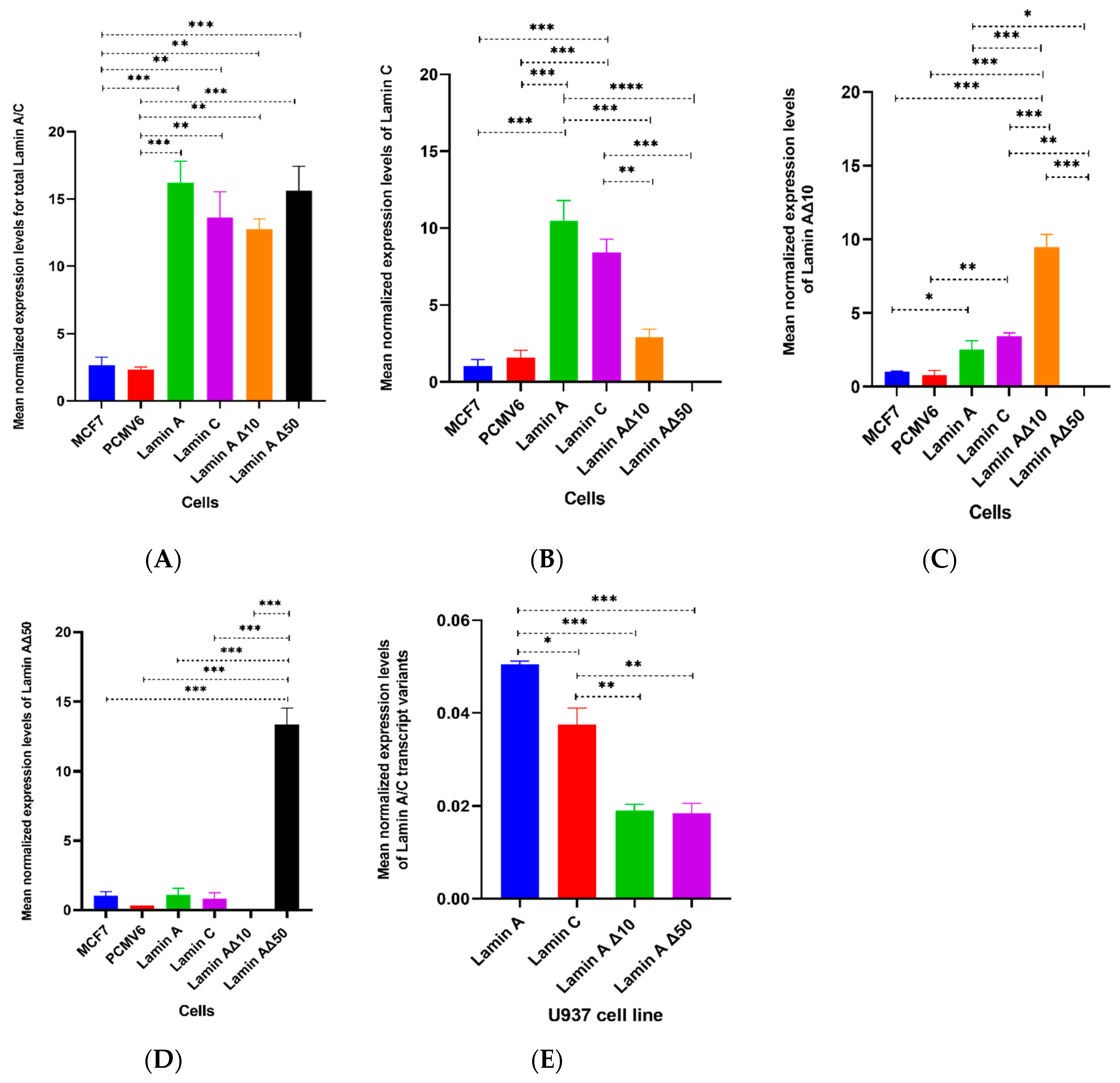
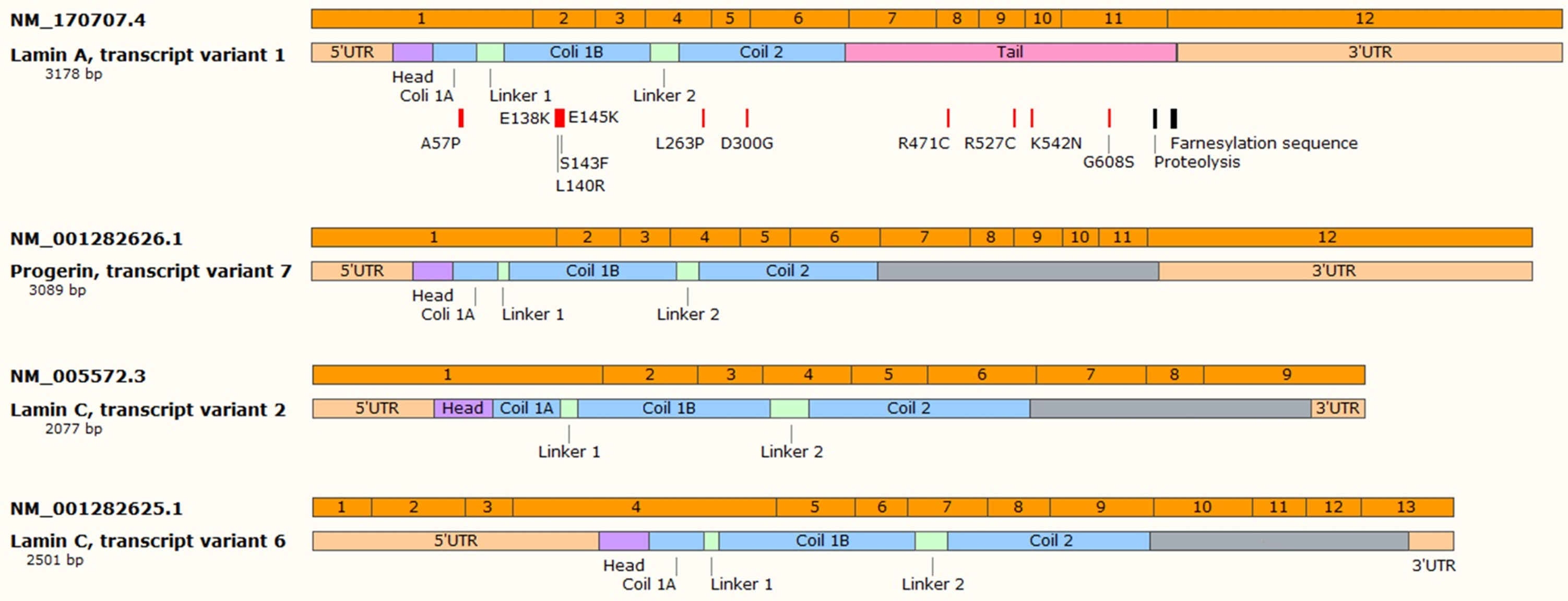
Increased expression of lamin b1 in drosophila melanogaster resulted in a degenerative phenotype. Vertebrate lamins consist of two types a and b. Lamin a c alternative splice variants lamin a lamin c lamin aδ10 and lamin aδ50 have been implicated in cell cycle regulation dna replication transcription regulation cellular differentiation apoptosis and aging. 2004 hypothesized that the alterations in nuclear structure are due to a concentration dependent dominant negative effect of la delta 50 leading to the disruption of lamin related functions ranging from the maintenance of nuclear shape to regulation of gene expression and dna replication.
Lamin proteins are thought to be involved in nuclear stability chromatin structure and gene expression. Lamin proteins are thought to be involved in nuclear stability chromatin structure and gene expression.