Lamin Cell Signaling
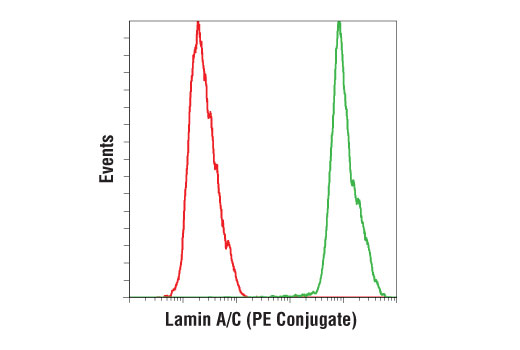
Type a lamins consist of lamin a and c which arise from alternative splicing of the lamin a gene lmna.
Lamin cell signaling. Lamins have been subdivided into types a and b. Type a lamins consist of lamin a and c which arise from alternative splicing of the lamin a gene lmna. Lamins have been subdivided into types a and b. Lamins have been subdivided into types a and b.
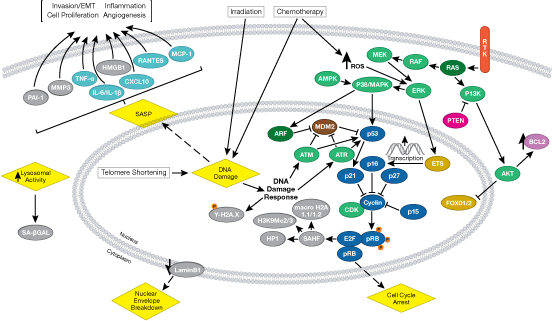
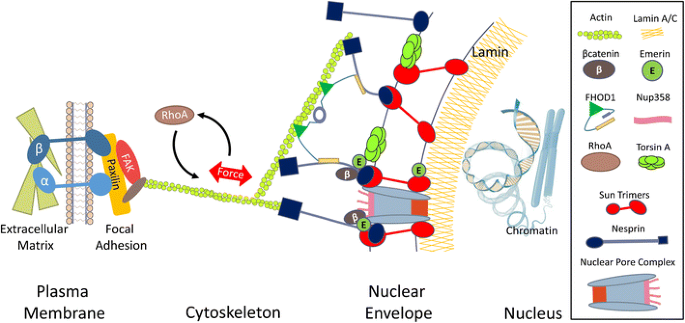
Lamins are nuclear membrane structural components that are important in maintaining normal cell functions such as cell cycle control dna replication and chromatin organization 1 3. Type a lamins consist of lamin a and c which arise from alternative splicing of the lamin a gene lmna. Lamins are nuclear membrane structural components that are important in maintaining normal cell functions such as cell cycle control dna replication and chromatin organization 1 3. Type a lamins consist of lamin a and c which arise from alternative splicing of the lamin a gene lmna.
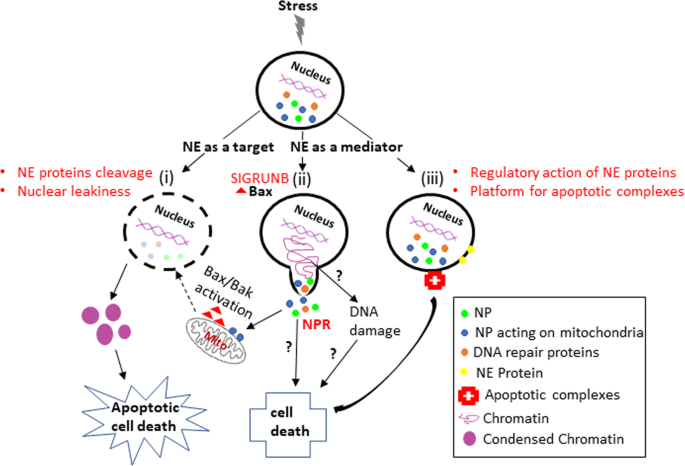
Lamins have been subdivided into types a and b. Type a lamins consist of lamin a and c which arise from alternative splicing of the lamin a gene lmna. Lamins are nuclear membrane structural components that are important in maintaining normal cell functions such as cell cycle control dna replication and chromatin organization 1 3. Lamin a c is cleaved by caspase 6 and.
Lamin a c is cleaved by caspase 6 and. Lamins are nuclear membrane structural components that are important in maintaining normal cell functions such as cell cycle control dna replication and chromatin organization 1 3. Lamins are nuclear membrane structural components that are important in maintaining normal cell functions such as cell cycle control dna replication and chromatin organization 1 3. Lamins have been subdivided into types a and b.
Lamin a c is cleaved by caspase 6 and serves as a marker for caspase 6 activation. Lamins are nuclear membrane structural components that are important in maintaining normal cell functions such as cell cycle control dna replication and chromatin organization 1 3. Lamins are nuclear membrane structural components that are important in maintaining normal cell functions such as cell cycle control dna replication and chromatin organization 1 3.