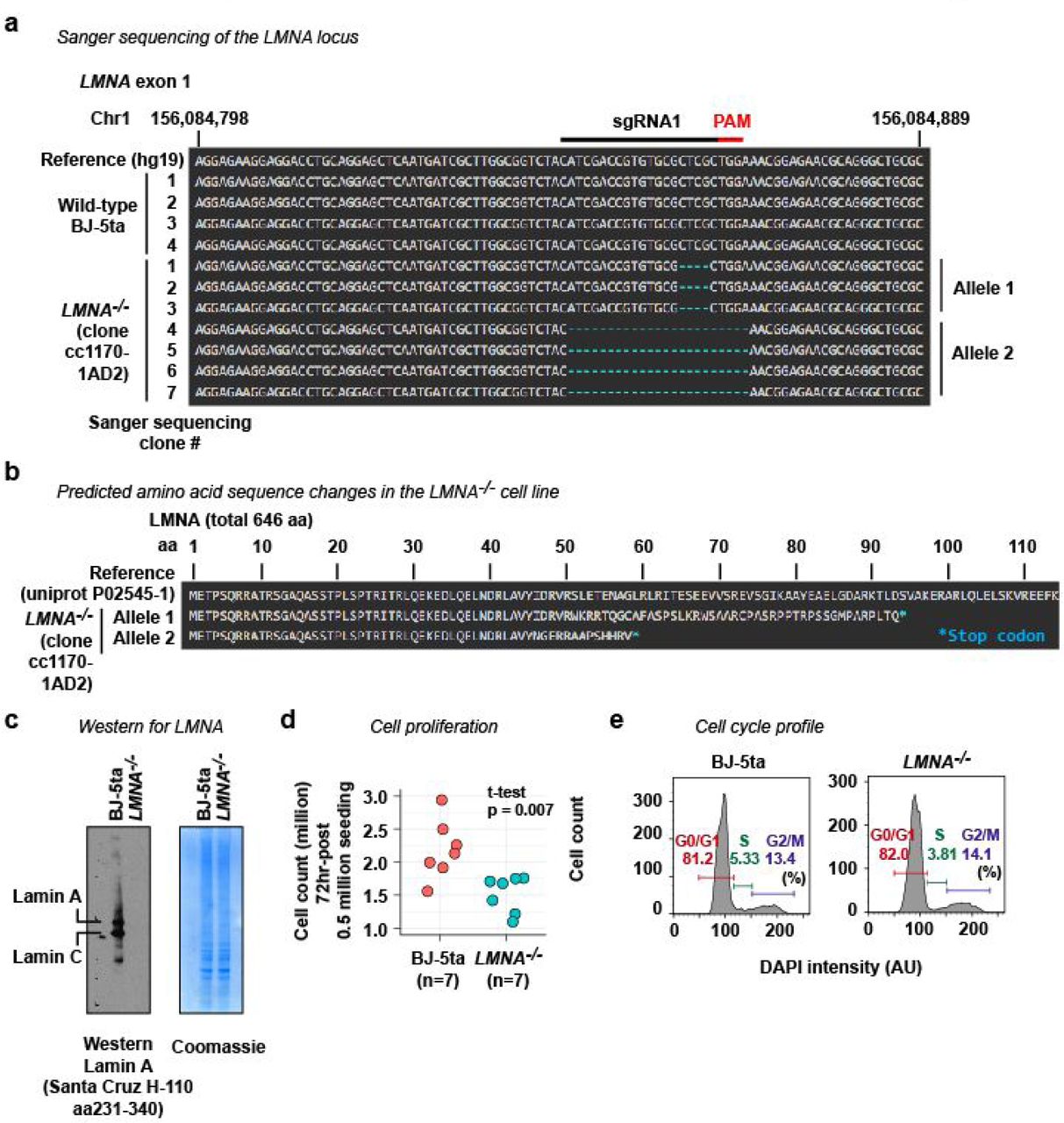
Lamin A Protein Sequence

P this section provides information about the protein and gene name s and synonym s and about the organism that is the source of the protein sequence p a href help names and taxonomy section target top more a p names taxonomy i.
Lamin a protein sequence. Lamins also known as nuclear lamins are fibrous proteins in type v intermediate filaments providing structural function and transcriptional regulation in the cell nucleus. The predicted protein lacks 30 amino acids in the lamin a tail which in full length lamin a contains an aspartic acid and glutamine rich stretch followed by 4 consecutive histidines. Variable lamin a delta 10 expression was detected in all cell lines and tissues examined. Phi blast performs the search but limits alignments to those that match a pattern in the query.
It stays associated with the membrane through protein protein interactions of itself and other membrane associated proteins such as lap1. Lamin a and c are present in equal amounts in the lamina of mammals. The lami n family of proteins make up the matrix and are highly conserved in evolution. The nuclear lamina consists of a two dimensional matrix of proteins located next to the inner nuclear membrane.
The nuclear lamina consists of a two dimensional matrix of proteins located next to the inner nuclear membrane. There are at least five different lamins in xenopus. Nuclear lamins interact with inner nuclear membrane proteins to form the nuclear lamina on the interior of the nuclear envelope. Lamin a is targeted to the nuclear membrane by an isoprenyl group but it is cleaved shortly after arriving at the membrane.
The lamin family of proteins make up the matrix and are highly conserved in evolution. Blastp simply compares a protein query to a protein database. Psi blast allows the user to build a pssm position specific scoring matrix using the results of the first blastp run. And the male germ cells lamin l iv.
During mitosis the lamina matrix is reversibly disassembled as the lamin proteins are phosphorylated. During mitosis the lamina matrix is reversibly disassembled as the lamin proteins are phosphorylated. While if proteins are evolutionary and structurally related they have limited sequence homologies except in several regions of the rod domain. Lamin proteins are thought to be involved in nuclear stability chromatin structure and gene expression.
Lamins are components of the nuclear lamina a fibrous layer on the nucleoplasmic side of the inner nuclear membrane which is thought to provide a framework for the nuclear envelope and may also interact with chromatin. Lamins have elastic and mechanosensitive properties and can alter gene regulation in a feedback response to mechanical cues. Plays an important role in nuclear assembly chromatin organization nuclear membrane and telomere dynamics. Depolymerization of the nuclear lamins leads to disintegration of the nuclear envelope.
The oocyte germinal vesicle lamin l iii. Lamin a is a 664 amino acid protein with a molecular weight of 70 kda calculated 74 139 da and a pi of 7 0 theoretical pi 7 4. The lamin family of proteins make up the matrix and are highly conserved in evolution. The ratio of lamin a to lamin a delta 10 varied among samples.