Lamin A Nuclear Rigidity Dahl Pajerowski

Pajerowski et al 2007.
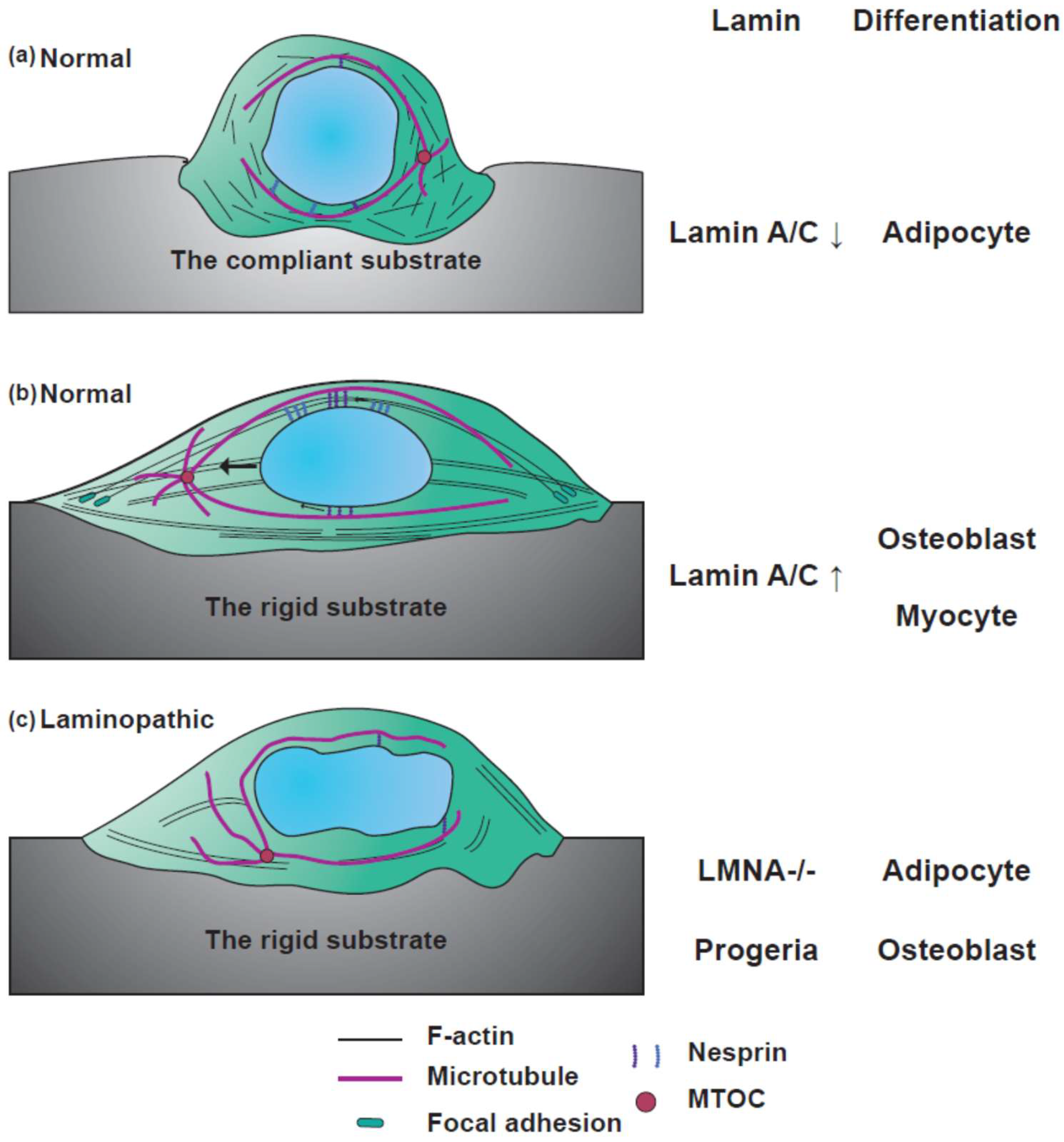
Lamin a nuclear rigidity dahl pajerowski. Decreased chromatin based nuclear mechanics results in abnormal nuclear ruptures and morphology. The nuclear lamina is a component of the nuclear envelope whose major structural element is a mesh of type v intermediate filament proteins called lamins. Left collagen and lamin a levels scale with e consistent with matching tissue stress to nuclear mechanics right matrix stiffness in tissue culture increases cell tension and stabilizes lamin a regulating its own transcription and that of stress fiber genes enhancing. A type lamins are mainly expressed in differentiated cells from the lmna gene that undergoes alternative splicing to form lamin a and lamin c.
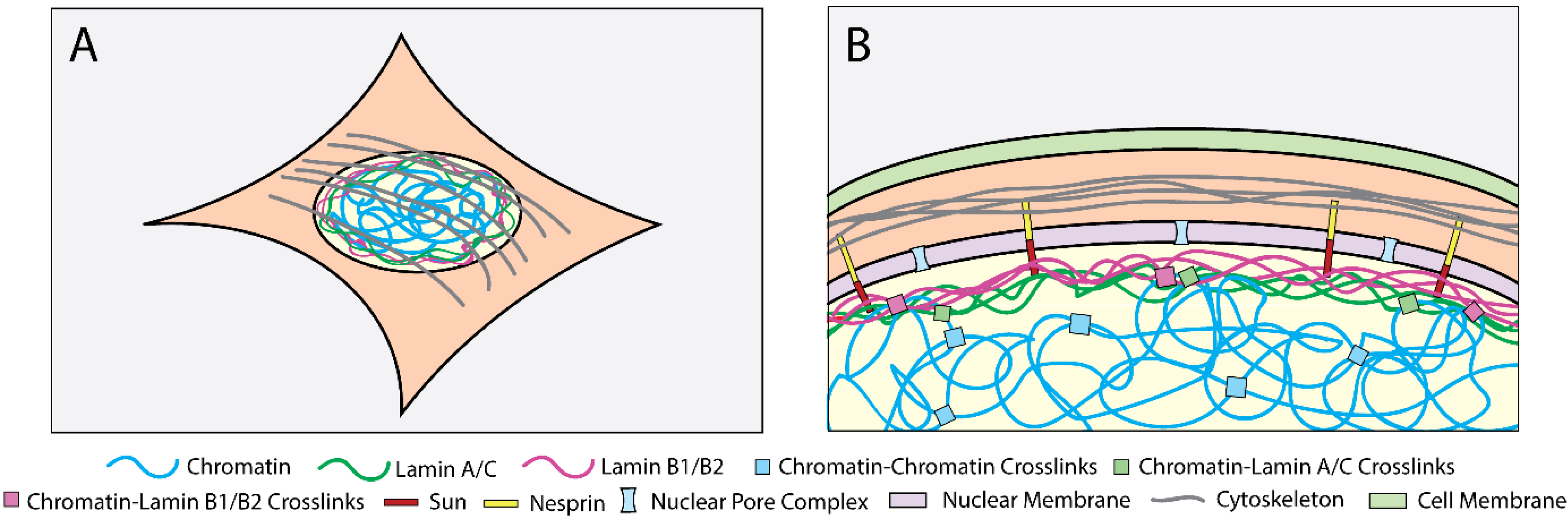
The nuclear lamina is composed mainly of type v intermediate filament proteins termed lamins which are classified into a and b type. Nuclear lamina proteins are type v intermediate filament proteins that exhibit important nuclear roles by contributing to structural integrity and regulating transcriptional activities dechat et al 2010 a type lamins are expressed from the gene lmna and include primarily lamin a and lamin c although other minority isoforms and splice variants occur naturally as well worman. Mutations within the la gene lmna lead to several human disorders most striking of which is hutchinson gilford progeria syndrome hgps a premature aging disorder. Loss of chromatin based rigidity has been shown to result in nuclear ruptures and increased dna damage independent of changes to lamins the current model is that the cytoskeleton compresses the nucleus while chromatin resists this compression to maintain compartmentalization measured commonly.
There are four major kinds of lamins which can be split into two types a and b types. 1 1 lamin a redistribution mediated by nuclear deformation determines dynamic 2 localization of yap 3 newsha koushki1 ajinkya ghagre1 luv kishore srivastava1 chris sitaras1 haruka yoshie1 clayton 4 molter1 and allen j. Rheologically lamin deficient states prove to be the most fluid like especially within the first 10 sec of deformation. We used aspiration of individual nuclei into micropipettes of diameter similar to the transwell pores in order to probe nuclear mechanics independent of cytoskeleton pajerowski et al 2007.
It is the most interior component of the nuclear envelope located underneath the inner nuclear membrane. B type lamins are ubiquitously expressed from the genes lmnb1 and lmnb2 to form the two main isoforms lamin b1 and b2. Because nuclear size does not change after lamin a knockdown we hypothesized that the rigidity of the nucleus is rate limiting to pore entry. Ehrlicher1 2 5 1department of bioengineering mcgill university montreal h3a 0e9 6 2department of anatomy and cell biology mcgill university montreal h3a 0c7.
Tissue micromechanics correlate with abundance of collagens and nuclear lamins which influence cell differentiation.